🤖 Summarize this article with AI:
💬 ChatGPT 🔍 Perplexity 💥 Claude 🐦 Grok 🔮 Google AI Mode
Low-code automation is revolutionizing the way businesses approach software development and process automation. By utilizing low-code platforms, organizations can streamline their workflows and enhance efficiency through the power of automation.
Low-code development tools provide a visual development environment with a drag-and-drop interface, enabling both developers and non-developers to create robust applications with minimal coding.
This approach accelerates the development process, allowing for rapid prototyping and deployment of business process automation solutions.
As companies grow, leveraging the right low-code software and automation tools is essential for optimizing business processes and achieving operational excellence. With use cases spanning various industries, low-code automation tools are becoming indispensable in the modern development environment.
🎯TL;DR | Low Code Automation
- Low-code automation streamlines development by enabling both developers and non-developers to create applications using visual, drag-and-drop interfaces, speeding up prototyping and deployment.
- Key benefits include faster development cycles, cost savings, increased accessibility for non-developers, and enhanced agility, making it easier for businesses to adapt to changes.
- Top low-code tools like Bugbug, Testim, Katalon Studio, TestProject, Cypress, and Leapwork offer various features and strengths, catering to different testing and automation needs across industries.
- Adoption of low-code automation is growing, driving innovation and efficiency in business processes, with platforms increasingly essential for achieving operational excellence.
Check also:
What Is Low Code Automation?
Low-code automation refers to the use of low-code platforms to design, develop, and deploy automated workflows and applications with minimal manual coding. These platforms provide visual development environments that allow users to create software solutions using drag-and-drop interfaces, pre-built components, and automated processes. Low-code automation simplifies the software development process, making it accessible to both professional developers and non-technical users.
Try low-code automation with BugBug
Test easier than ever with BugBug test recorder. Faster than coding. Free forever.
Get started
Key features of low-code test automation tools include:
- Visual Development Environment: Users can build applications through intuitive visual interfaces, reducing the need for extensive coding knowledge.
- Drag-and-Drop Interface: This feature enables users to easily configure workflows and applications by dragging and dropping elements into place.
- Pre-built Components: Low-code platforms often come with a library of pre-built components and templates that users can leverage to accelerate development.
- Integration Capabilities: These platforms can integrate with various software systems and data sources, allowing for seamless automation of business processes.
- Rapid Prototyping and Deployment: Low-code automation speeds up the development cycle, enabling quick prototyping, testing, and deployment of applications.
- Scalability: Solutions built with low-code tools can scale to meet the growing needs of businesses.
- Collaboration: Low-code platforms facilitate collaboration between IT and business teams, ensuring that applications meet business requirements while adhering to technical standards.
By using low-code automation, organizations can efficiently automate repetitive tasks, improve operational efficiency, and drive digital transformation. This approach empowers businesses to respond swiftly to changing market demands and optimize their processes for better performance and productivity.
👉 Check also our ultimate guide on Codeless Automation Testing.
Benefits of Low Code Test Automation Tools
Low-code automation offers numerous advantages for businesses, enhancing efficiency and agility in operations. Here’s why adopting low-code automation is beneficial:
- Faster Development Cycles:
- Low-Code Development Platform: Using a low-code development platform accelerates application development by reducing the need for extensive coding.
- Rapid Prototyping: Businesses can quickly develop and iterate on low-code applications, bringing products to market faster.
- Cost Savings:
- Reduced Development Costs: Low-code solutions lower the need for specialized software developers, cutting down costs.
- Lower Maintenance Costs: Low-code application development platforms often include built-in maintenance, reducing ongoing support expenses.
- Accessibility for Non-Developers:
- Empowerment: Low-code and no-code platforms empower business users to create and modify applications without deep technical skills.
- User-Friendly Interfaces: Low-code platforms use intuitive drag-and-drop interfaces, making it easy for non-developers to build applications.
- Enhanced Agility:
- Adaptability: Low-code automation helps businesses quickly adapt to changing requirements with minimal disruption.
- Scalability: Low-code application platforms can scale easily to meet growing business needs.
- Improved Collaboration:
- Cross-Functional Teams: Low-code platforms enable better collaboration between IT and business teams on automation projects.
- Unified Development Environment: A single, integrated environment streamlines communication and project management.
- Integration Capabilities:
- Seamless Integration: Low-code development platforms offer pre-built connectors and APIs, facilitating integration with existing systems.
- Data Connectivity: Efficiently connect and leverage data from various sources for enhanced workflow automation.
- Increased Innovation:
- Experimentation: The reduced cost and ease of use of low-code tools encourage experimentation and innovation.
- Customization: Low-code technology allows for customization to meet specific business needs, providing tailored low-code solutions.
- Governance and Compliance:
- Built-In Security: Many low-code platforms offer built-in security features, ensuring compliance with regulatory standards.
- Governance Tools: Features like version control and audit trails ensure secure and effective management of low-code applications.
- Automation Capabilities:
- Task Automation: Low-code platforms enable simple task automation, streamlining routine processes.
- Enterprise Process Automation: Low-code process automation can handle complex, enterprise-wide workflows, improving efficiency.
- Robotic Process Automation: Integrating robotic process automation with low-code platforms enhances automation capabilities.
By adopting low-code and codeless test automation platforms, organizations can save time, reduce costs, and empower a broader range of users to participate in the application development process, leading to more efficient and agile operations.
👉 Check how easy you can start your test automation journey with BugBug - Beginners tutorial to automation testing
How to Start With Low-code Workflow Automation?
Starting with low-code workflow automation involves several steps to ensure successful implementation and maximize the benefits of this technology. Here's a comprehensive guide to get you started:
1. Understand Your Needs and Objectives
- Identify Business Processes: Begin by identifying the processes that need automation. Focus on repetitive, time-consuming tasks that can benefit from automation.
- Set Clear Goals: Define what you aim to achieve with low-code automation. Goals might include increasing efficiency, reducing errors, or improving workflow transparency.
2. Select the Right Low-Code Platform
- Evaluate Options: Research and evaluate different low-code automation platforms based on your needs. Consider factors like ease of use, integration capabilities, scalability, and cost.
- Trial and Demos: Take advantage of free trials and demos to see how different platforms work and which one best suits your requirements.
3. Plan Your Automation Strategy
- Prioritize Processes: Prioritize which workflows to automate first based on their impact and complexity. Start with simple processes before moving on to more complex ones.
- Map Out Workflows: Create detailed maps of your current workflows. This helps in understanding each step and identifying areas for improvement.
4. Develop and Design Workflows
- Use Drag-and-Drop Interfaces: Utilize the low-code platform's drag-and-drop interface to design workflows. These tools often allow you to build processes visually without writing a single line of code.
- Incorporate Business Logic: Define rules and conditions within your workflows to ensure they operate correctly. This might include setting up approvals, notifications, and data validations.
5. Integrate with Existing Systems
- Use Pre-Built Connectors: Many low-code platforms come with pre-built connectors to integrate with existing systems (e.g., CRM, ERP, databases). Leverage these for seamless data flow.
- Custom Integrations: If necessary, create custom integrations using the platform's API capabilities to connect with other software tools.
6. Test Your Workflows
- Low-Code Test Automation: Use the platform's testing features to simulate workflow processes and identify any issues. This ensures your workflows are robust and error-free before going live.
- User Testing: Involve end-users in testing to get feedback and make necessary adjustments. This helps in aligning the workflows with actual user needs.
7. Deploy and Monitor
- Gradual Rollout: Deploy the automated workflows gradually. Start with a small group of users and expand as confidence in the system grows.
- Monitor Performance: Continuously monitor the performance of your automated workflows. Use the platform's analytics and reporting tools to track key metrics and identify areas for improvement.
8. Iterate and Improve
- Feedback Loop: Establish a feedback loop with users to gather insights and suggestions for further improvements.
- Regular Updates: Keep refining and updating your workflows based on feedback and changing business needs.
9. Train Your Team
- User Training: Provide training sessions for users to familiarize them with the new automated workflows. Ensure they understand how to interact with the system and report any issues.
- Ongoing Support: Offer ongoing support to address any questions or problems that arise after deployment.
10. Scale and Expand
- Expand Automation: Once initial workflows are running smoothly, gradually expand automation to other areas of the business.
- Leverage Advanced Features: As you become more comfortable with the platform, explore and leverage advanced features like AI and machine learning to further enhance your workflows.
By following these steps, you can effectively start with low-code workflow automation, streamlining your business processes and enhancing overall efficiency.
Automate your tests for free
Test easier than ever with BugBug test recorder. Faster than coding. Free forever.
Get started
Top Low Code Test Automation Tools
When selecting low-code automation solution, prioritize ease of use with intuitive interfaces and minimal learning curves to accommodate both technical and non-technical users.
👉 Ensure integration capabilities, including API integration and pre-built connectors, to seamlessly connect with existing systems.
👉 Look for scalable solutions that can handle increasing workloads and offer customization options to tailor workflows to your specific needs.
👉 Security and compliance features are crucial, so choose tools that adhere to industry standards and regulations.
👉 Reliable customer support and a strong user community can provide valuable resources and assistance.
👉 Comprehensive analytics and reporting tools are essential for monitoring performance and optimizing processes.
👉 Lastly, evaluate the cost and licensing model to ensure it fits within your budget while providing the necessary features and flexibility.
💡 Check also our guide on No-code Automation Testing
Here are few popular low-code tool choices:
BugBug
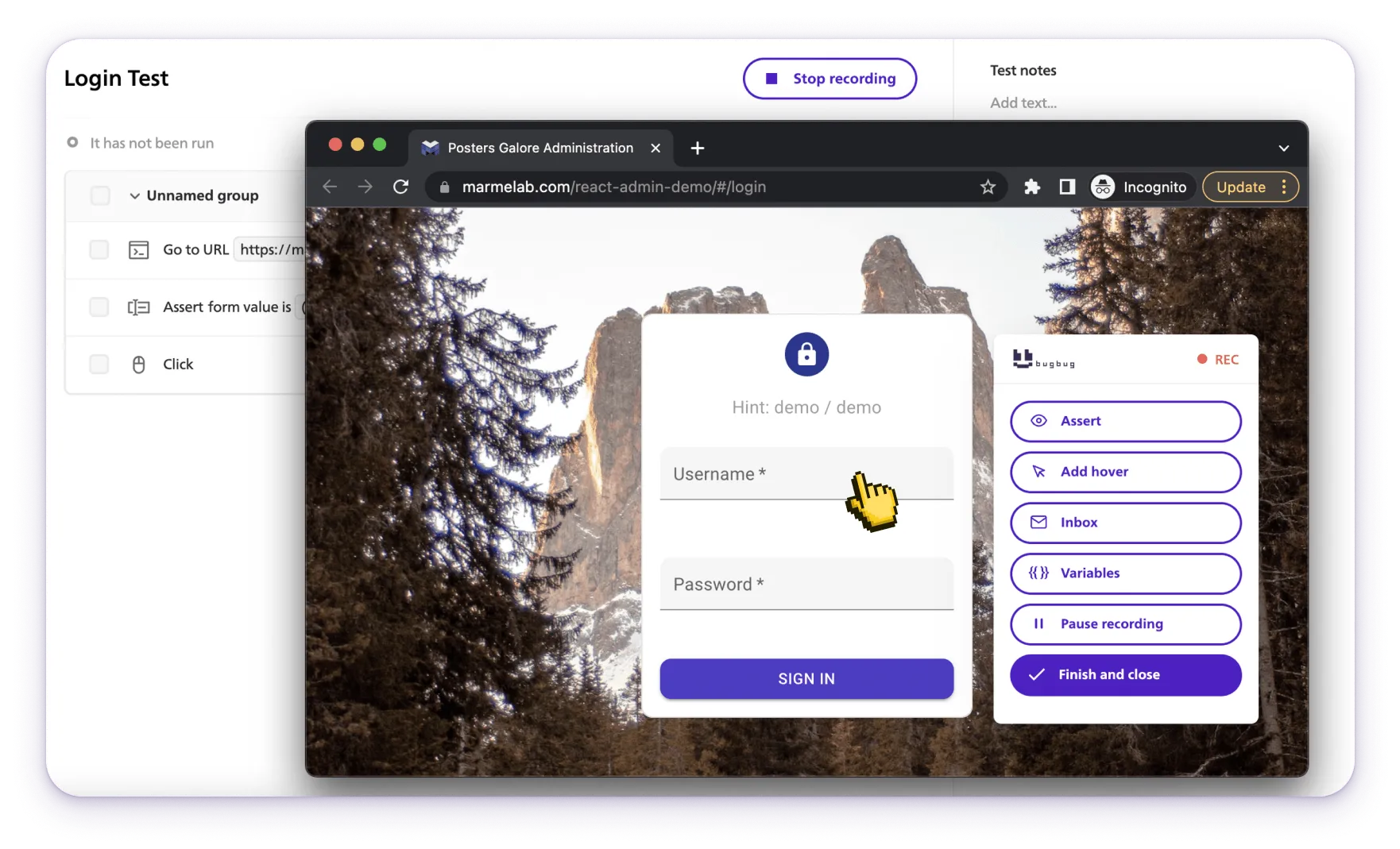
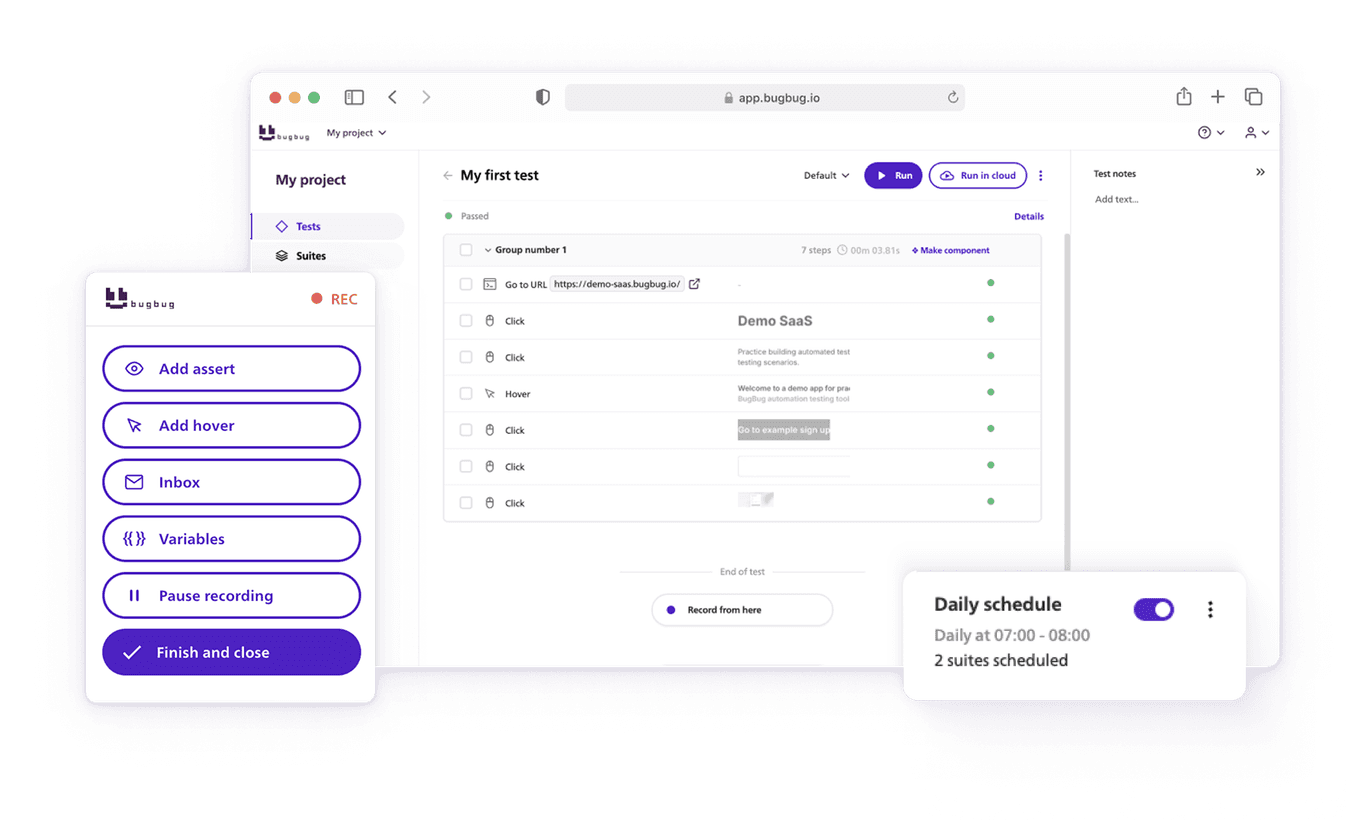
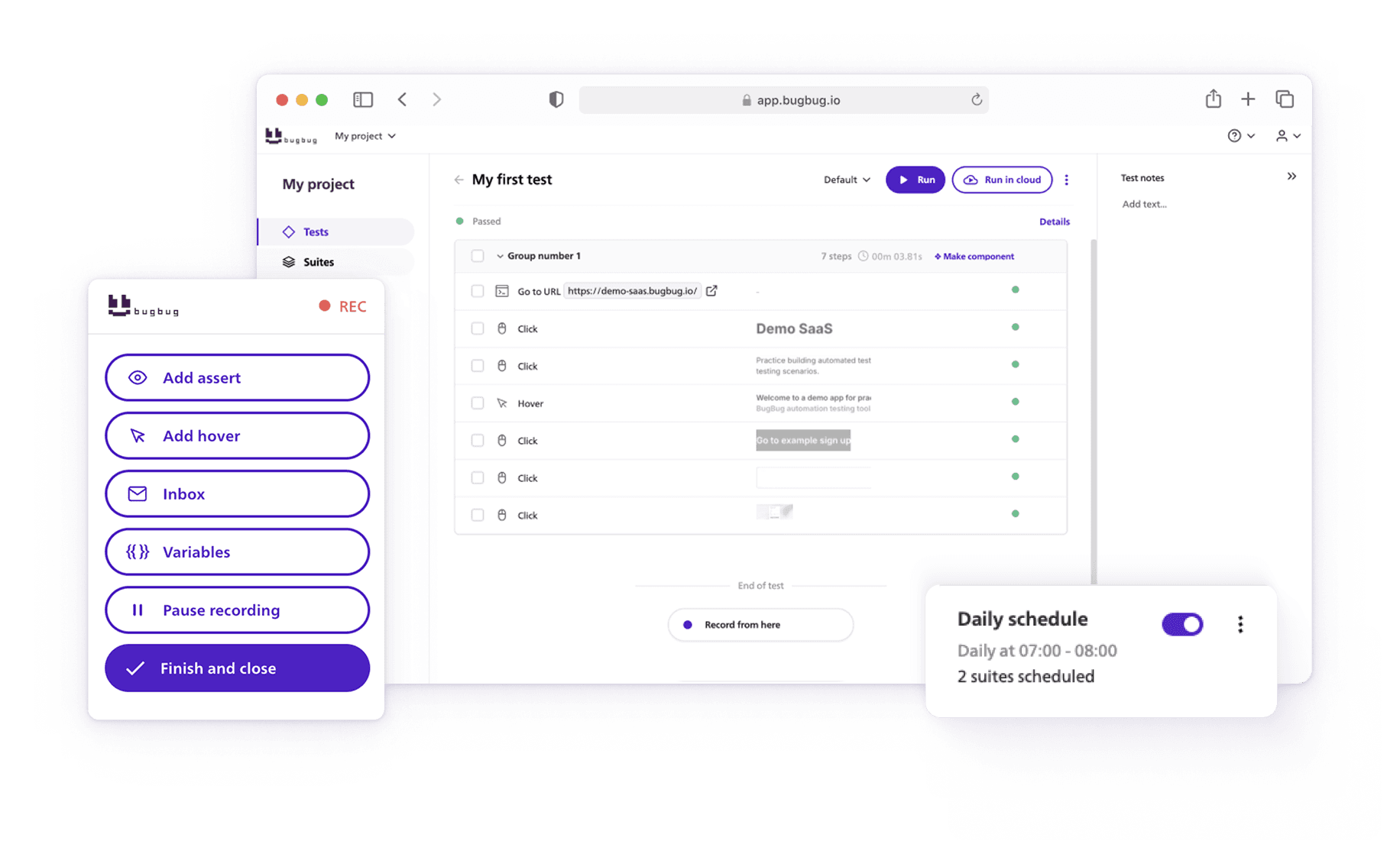
Bugbug is a low-code test automation tool designed for end-to-end testing of web applications. It allows users to create tests without any programming knowledge, making it accessible to both developers and non-developers.
The tool is known for its simplicity and efficiency, especially in creating and running automated tests directly from the browser.
Key Features:
👾 No-code/Low-code Test Creation: Easily create tests through a user-friendly interface without writing code.
👾 Automated Browser Testing: Run tests directly in the browser to simulate user interactions.
👾 Test Maintenance: Automatically updates tests when changes are detected in the web application.
👾 Test Analytics: Provides insights into test performance and failure analysis.
👾 Continuous Integration (CI) Integration: Integrates with popular CI tools for seamless automated testing in deployment pipelines.
Strengths:
- Ease of Use: Simple to use, making it ideal for teams with limited coding expertise.
- Quick Setup: Allows rapid creation and execution of tests.
- Browser Compatibility: Supports major browsers, ensuring broad test coverage.
- Cost-effective: Offers a free plan with essential features, suitable for small teams.
Limitations:
- Limited Advanced Features: May not have the advanced customization and scripting capabilities that developers may require for complex scenarios.
- Scalability: May not be suitable for very large-scale enterprise applications with highly complex testing needs.
Use Cases:
- Small to medium-sized teams needing quick, low-code test automation.
- Testing web applications where frequent updates require easy maintenance of test cases.
- Teams integrating automated testing into CI/CD pipelines without extensive coding knowledge.
BrowserStack
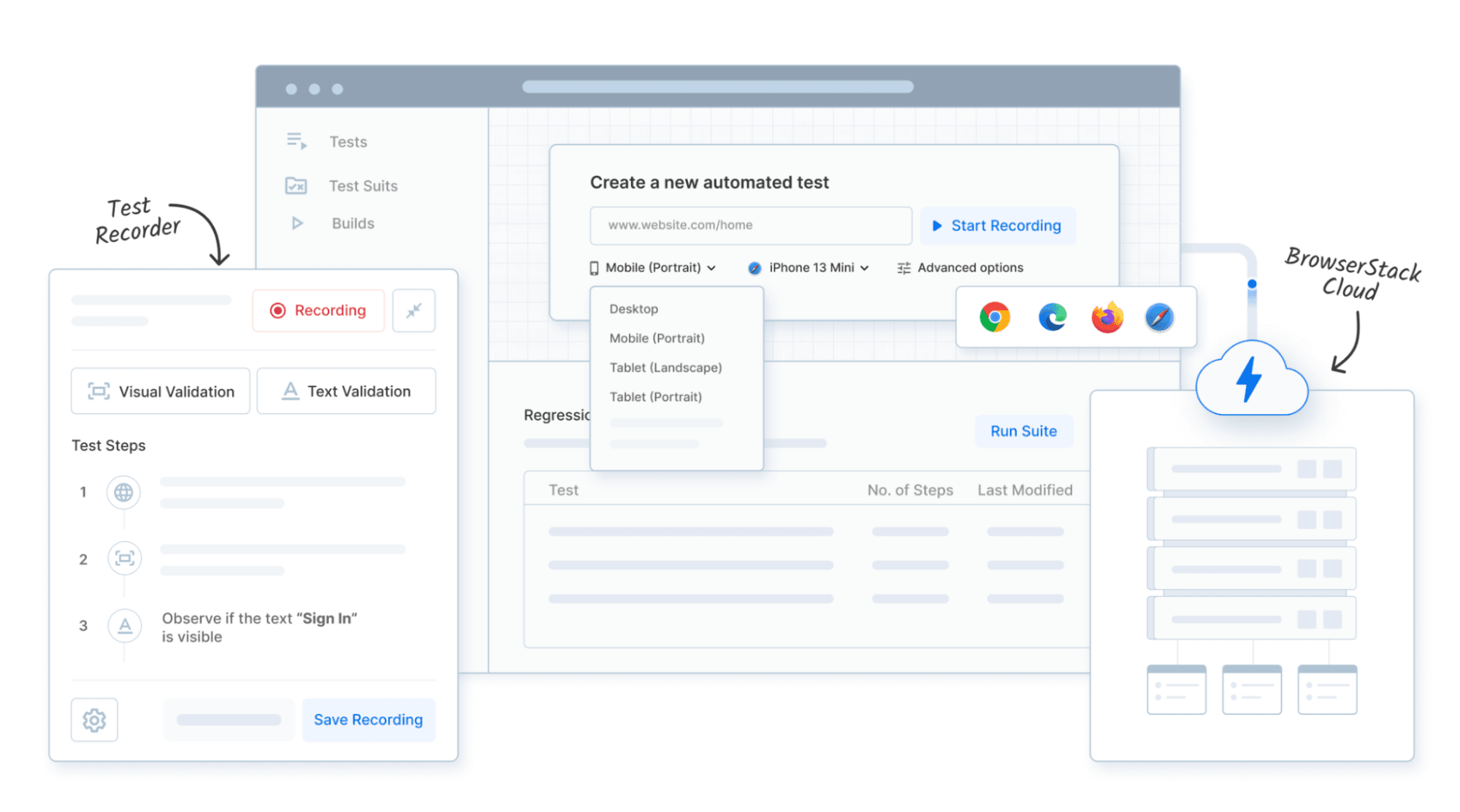
BrowserStack Low-Code Automation lets teams create, run, and maintain automated tests without writing code. With an interactive recorder, AI-powered self-healing, and real-device cloud testing, teams can start automation in minutes and scale across browsers and devices.
The team claims to speed up test creation by 10x and cut build failures by up to 40%, via low-code authoring and AI-driven self-healing to enable faster, reliable releases.
Key Features
- AI-Powered Self-Healing: Detects changes in UI elements and automatically updates test steps, reducing flaky failures.
- Visual Validation: Insert visual checkpoints to confirm that UI components and screens render correctly, to ensure consistent appearance across devices and browsers.
- Data-Driven Testing: Execute the same test with multiple input sets to increase coverage without duplicating test scripts.
- Reusable Test Modules: Store commonly used actions (like login or checkout flows) as reusable components to simplify maintenance across large suites.
- CI/CD Integration & Scheduling: Automate test execution by integrating with build pipelines or scheduling runs to enable continuous testing.
Strengths:
- Test Editing Without Re-Recording: Update, add, or remove steps directly within an existing test, eliminating the need to start over and making maintenance faster and easier.
- Ease of Use: Minimal coding required, making it accessible to non-technical users.
- Scalability: Suitable for teams of all sizes, from startups to enterprises.
- Extensive Integration: Seamlessly integrates with popular CI/CD tools, project management tools and test frameworks.
Weakness:
- Free Plan: Free plan does not offer advanced capabilities and can feel limited for growing teams relying only on it.
Use Cases:
- Businesses of all sizes seeking an automation solution that balances simplicity with powerful testing features.
- Non-technical users who want to create and maintain tests without coding.
- Companies aiming to speed up release cycles while maintaining software quality.
- Teams needing to perform cross-platform, cross-browser, and visual testing at scale.
Testim

Testim is an AI-driven, low-code test automation tool that allows users to create stable and scalable automated tests for web applications. It leverages machine learning to maintain tests, reducing the need for manual intervention.
Key Features:
- AI-powered Test Stability: Uses AI to analyze and adapt to changes in the application’s UI.
- Visual Test Editor: A low-code interface for creating and managing tests.
- Self-healing Tests: Automatically updates tests when application changes are detected.
- Test Management: Offers robust test organization, version control, and analytics.
- Integration: Works seamlessly with popular CI/CD tools and version control systems.
Strengths:
- AI-driven: Reduces test maintenance effort through self-healing tests.
- Scalability: Can handle complex test scenarios and large-scale applications.
- Ease of Use: Low-code interface that requires minimal coding.
- Extensive Integrations: Easily integrates with existing development and CI/CD workflows.
Limitations:
- Learning Curve: While it’s low-code, some features might require understanding AI behavior and settings.
- Cost: Can be expensive for smaller teams or startups.
Use Cases:
- Enterprises needing to maintain large test suites with frequent updates.
- Teams wanting to leverage AI to reduce test maintenance time.
- Testing web applications with complex workflows.
Katalon Studio

Katalon Studio is a comprehensive low-code automation testing tool that supports web, API, mobile, and desktop application testing. It offers both a low-code interface and scripting capabilities, making it suitable for a wide range of testing scenarios.
Key Features:
- All-in-One Platform: Supports web, API, mobile, and desktop testing.
- Low-Code and Scripting: Provides a low-code interface for beginners and a scripting mode for advanced users.
- Built-in Keywords: Comes with a library of built-in keywords to simplify test creation.
- Data-driven Testing: Supports parameterized tests with external data sources.
- Reporting: Detailed reporting and analytics features.
Strengths:
- Versatility: Supports multiple platforms and types of testing.
- Community and Support: Strong community and extensive documentation.
- Ease of Use: Low-code features combined with powerful scripting options.
- Cost-effective: Offers a free version with essential features.
Limitations:
- Performance: May experience performance issues with very large test suites.
- Complexity: Advanced features may require a learning curve.
Use Cases:
- Testing web, mobile, API, and desktop applications in a single platform.
- Teams with both non-developers and developers needing a flexible testing tool.
- Projects requiring data-driven testing and robust reporting.
TestProject

TestProject is a free, low-code test automation platform that supports web, mobile, and API testing. It’s cloud-based and designed to be collaborative, making it ideal for teams.
Key Features:
- Cross-platform Support: Supports web, mobile, and API testing.
- Low-code Test Creation: Drag-and-drop interface for creating tests.
- Community Add-ons: Access to a large library of community-built test components.
- CI/CD Integration: Easily integrates with CI/CD pipelines.
- Cloud-based: Allows collaboration and test management from anywhere.
Strengths:
- Free and Open: Fully free with robust features.
- Collaboration: Cloud-based nature facilitates team collaboration.
- Ease of Use: Intuitive interface for non-technical users.
- Community Support: Strong community with shared add-ons.
Limitations:
- Cloud Dependency: Requires internet access for full functionality.
- Limited Advanced Features: May lack some advanced features needed for complex enterprise-level testing.
Use Cases:
- Teams needing a free, collaborative, and cloud-based testing solution.
- Web, mobile, and API testing across different platforms.
- Projects with distributed teams needing easy collaboration on test cases.
Cypress

Cypress is a fast and reliable testing tool for web applications. While it’s primarily code-based, it offers low-code features and is widely appreciated for its simplicity and speed, making it a favorite among front-end developers.
Key Features:
- Real-time Reloads: Automatically reloads when changes are made.
- Time Travel: Debugging made easy with snapshots taken as your tests run.
- Dashboard Service: Provides advanced test analytics and management.
- Cross-browser Testing: Supports multiple browsers for comprehensive testing.
- Fast and Reliable: Optimized for speed and reliability in testing.
Strengths:
- Developer-Friendly: Integrated well with the development process.
- Speed: Tests run quickly and efficiently.
- Ease of Debugging: Excellent debugging tools with time travel and real-time reloading.
- Strong Community: Active community providing plugins and support.
Limitations:
- Learning Curve: Primarily code-based, which might be challenging for non-developers.
- Limited Mobile Support: Focused mainly on web applications.
Use Cases:
- Front-end developers needing a fast and reliable testing tool.
- Testing web applications across different browsers.
- Teams requiring detailed debugging capabilities.
Leapwork

Leapwork is a powerful, visual, no-code automation platform that allows both technical and non-technical users to create automated tests for various applications, including web, desktop, and APIs.
Key Features:
- Visual Flow Creation: No-code automation through a flowchart-like interface.
- Cross-Platform Testing: Supports web, desktop, and API testing.
- Integration: Integrates with popular CI/CD tools and other enterprise systems.
- Reporting and Analytics: Provides detailed insights into test execution.
- Reusable Components: Allows the creation of reusable components for tests.
Strengths:
- No-Code: True no-code platform, enabling non-technical users to create tests.
- Scalability: Suitable for enterprise-level applications.
- Extensive Integrations: Works well within existing enterprise ecosystems.
- User-Friendly: Visual approach makes it easy to use and understand.
Limitations:
- Cost: Higher price point, particularly for small teams or startups.
- Performance: May experience performance issues with highly complex tests.
Use Cases:
- Large enterprises needing scalable test automation across different platforms.
- Teams with non-technical users requiring a no-code automation solution.
- Projects that require reusable components and integrations with enterprise systems.
Automate your tests for free
Test easier than ever with BugBug test recorder. Faster than coding. Free forever.
Get started
Final Thoughts on Low-Code Test Automation Tools
The benefits of low-code automation are vast, ranging from rapid low-code app development to seamless integration of complex business processes using a low-code platform. Low-code automation tools make it possible to implement robust solutions with minimal application code, thus saving time and resources. Various low-code automation use cases, such as workflow automation and process optimization, highlight the transformative power of these platforms. The key difference between low-code and no-code lies in the level of customization and coding required, but both offer substantial advantages. Using low-code automation tools, businesses can expedite their digital transformation journey, enabling faster deployment of applications and better scalability. Ultimately, low-code automation platforms enable organizations to harness the full potential of automation, driving innovation and ensuring a competitive edge in the market.
Happy (automated) testing!