- 🎯 TL;DR - Ecommerce Website Guide
- What is ECommerce Website Testing?
- What Are the Challenges of E-Commerce Testing?
- What Should You Know Before Running an E-Commerce Test?
- Checklist for Testing an E-commerce Site
- What Are the Essential Test Cases for an E-Commerce Website?
- Tools for E-Commerce Testing
- How to Automate E-Commerce Testing?
- Conclusion
- FAQ - E-commerce Testing
🤖 Summarize this article with AI:
💬 ChatGPT 🔍 Perplexity 💥 Claude 🐦 Grok 🔮 Google AI Mode
E-commerce websites operate in a high-stakes environment where every click, scroll, and checkout directly impacts revenue. To meet rising customer expectations, teams must go beyond ad-hoc checks and commit to rigorous testing strategies that cover all critical flows. From user interface testing to scalability testing, from app testing to cross device compatibility, the goal is to deliver a smooth user experience across multiple devices and multiple browsers.
🎯 TL;DR - Ecommerce Website Guide
- Why it matters: E-commerce testing protects revenue by validating critical flows (search → cart → checkout → payment), covering functionality, performance, security, accessibility (WCAG), and cross-device/cross-browser behavior.
- Key challenges: Complex third-party integrations (payments, shipping, CRM) and realistic user scenarios make compatibility, data integrity, and scale hard to test without a structured approach.
- Prep first: Set clear objectives, understand the platform, prepare realistic test data, choose tooling, mirror prod in staging, define benchmarks, align with stakeholders, and include PCI/data-protection checks.
- What to test: Homepage/navigation, product pages, cart, checkout, payments, post-purchase, accounts—plus non-functional suites: performance/load, mobile responsiveness, cross-browser, accessibility, and security.
- How to execute: Run automated tests (ideally via CI/CD) for regression on revenue paths; use a codeless tool like BugBug to record and maintain flows quickly, then add exploratory/manual spot-checks and iterate as the store evolves.
Check also:

Test Your E-Commerce Website with BugBug
Test easier than ever with BugBug test recorder. Faster than coding. Free forever.
Get started
What is ECommerce Website Testing?
Ecommerce testing is a critical component in the development and maintenance of online shopping platforms. It involves a series of processes and methodologies aimed at ensuring that an e-commerce site is not only functional but also secure, user-friendly, and capable of handling the demands of its users efficiently. E-commerce software testing is distinct from general website testing because it specifically simulates user interactions such as browsing, checkout, and payment processing to ensure a seamless shopping experience unique to online retail.
This type of testing analyzes every aspect of the e-commerce experience, from the initial landing page to the final checkout process, to identify any potential issues that could affect the performance, security, or overall user satisfaction. E-commerce testing requires a comprehensive strategy that includes functional, performance, security, and compatibility testing to ensure a seamless and secure user experience.
Why Test Ecommerce Websites?
At its core, e-commerce website testing focuses on several key areas:
- Functionality Testing: Ensuring that all features of the website work as intended. This includes testing product search capabilities, product filters, add-to-cart functionality, checkout processes, payment gateway integration, and more.
💡 Check also our guide on the best Functional Testing Tools.
- Usability Testing: Evaluating the website from the user's perspective to ensure it is intuitive, easy to navigate, and provides a positive shopping experience.
- Performance Testing: Assessing the website's speed and responsiveness under various conditions. This includes load testing to determine how the site performs under heavy traffic and stress testing to see how much load it can handle before it becomes unresponsive.
- Security Testing: Critical for e-commerce sites due to the handling of sensitive customer information and financial transactions.
- Mobile Responsiveness: Testing for mobile responsiveness ensures the site is optimized for various screen sizes and operating systems, providing a seamless experience for mobile users.
- Compatibility Testing: Ensuring the e-commerce site works across different browsers, operating systems, and devices, thereby maximizing its accessibility to a wider audience.
What Are the Challenges of E-Commerce Testing?
E-commerce testing presents a unique set of challenges that stem from the complexity and dynamic nature of online shopping platforms. Understanding user behavior and considering various user scenarios are essential to address the unique challenges of e-commerce testing. These challenges are critical to address for ensuring the reliability, performance, and security of e-commerce websites. Let’s delve into some of the key challenges involved in e-commerce testing:
Ensuring a Seamless User Experience Across Devices and Platforms
With the variety of devices, operating systems, and browsers that customers use to access e-commerce sites, ensuring a consistent and seamless user experience across all platforms is a significant challenge. This requires comprehensive compatibility testing, which can be time-consuming and resource-intensive.
Complex Integration with Multiple Systems
E-commerce platforms integrate with numerous external systems, including payment gateways, shipping services, inventory management systems, and customer relationship management (CRM) tools. Ensuring seamless integration and communication between these systems requires extensive API and integration testing.
Testing Under Real-World Conditions
Simulating real-world shopping scenarios to test the website's functionality, performance, and usability can be challenging. This includes testing for various user behaviors, payment methods, shipping options, and handling returns or cancellations.
What Should You Know Before Running an E-Commerce Test?
Before starting e-commerce testing, preparation is everything. A structured plan ensures thorough testing, reduces missed issues, and helps deliver a smooth user experience. Here are the essentials to cover before you begin:
1. Define Clear Objectives
Set goals for testing — from verifying functionality to improving performance, usability, and security. Clear objectives keep efforts focused.
2. Understand Your Platform
Know your e-commerce platform’s architecture, features, and integrations. This helps identify where testing should focus most.
3. Map Users and Use Cases
Define your audience and simulate real-world shopping flows like browsing, adding items to cart, and checkout.
4. Build a Testing Checklist
Cover all types of testing: functional, usability, security, performance, and cross-device testing.
5. Prepare Realistic Test Data
Use product info, sandbox payments, and shipping details to mirror real user interactions.
6. Select the Right Tools
Choose tools for automated tests, regression, performance analysis, and vulnerability checks.
7. Set Up Test Environments
Use staging or pre-production environments that mimic live conditions to catch issues early.
8. Define Benchmarks
Establish speed and load-time targets to guide performance testing.
9. Check Security and Compliance
Include PCI DSS and data protection standards in your test plan to prevent breaches.
10. Involve Stakeholders
Align testing with business priorities by engaging developers, PMs, and owners.
12. Train Your Team
Make sure testers understand both the platform and chosen tools. Fill knowledge gaps before execution.
Checklist for Testing an E-commerce Site
A comprehensive checklist for testing an e-commerce site includes:
- [ ] Homepage and Navigation: Ensure the homepage loads correctly, and navigation links work as expected.
- [ ] Product Pages: Verify that product information is accurate, images load, price details and currency are correct.
- [ ] Search Functionality: Test the search feature for accuracy and speed.
- [ ] Shopping Cart: Check that items can be added, updated, or removed from the cart smoothly.
- [ ] Checkout Process: Ensure the checkout process is seamless, from entering shipping details to completing payment.
- [ ] Payment Gateway: Test different payment methods for successful transactions and error handling.
- [ ] Account Creation and Management: Verify account registration, login, password recovery, and profile updates.
- [ ] Responsiveness: Assess the site’s performance on various devices and screen sizes.
- [ ] Security: Check for SSL certificate implementation, data encryption, and secure payment processing.
- [ ] Broken Links: Identify and fix broken links and redirects to ensure a seamless user experience.
- [ ] Accessibility Testing: Use tools (such as BrowserStack) to identify WCAG violations and ensure website inclusivity and compliance across different browsers and devices.
💡 Check also our guide on Shopify Testing.
What Are the Essential Test Cases for an E-Commerce Website?
Testing an e-commerce site is different from testing a blog, SaaS dashboard, or internal tool. Every bug risks lost revenue, frustrated customers, and brand damage. That’s why defining essential test cases is step one before you even think about automation.
Below, I’ve grouped the must-have e commerce test cases into categories that cover the entire user journey — from browsing to checkout to post-purchase interactions.
Homepage & Navigation
- Homepage load test: Verify the homepage loads correctly and quickly.
- Search bar: Ensure users can search by keyword, product name, and category.
- Navigation menu: Check categories, subcategories, and filters work as expected.
- Promotions & banners: Validate that promotional links and discount banners lead to correct landing pages.
Product Pages
- Product details: Confirm correct display of name, description, price, and availability.
- Images & gallery: Test image zoom, carousel, and alternate product views.
- Variants: Ensure size, color, and style selections update availability and price accurately.
- Add to wishlist / favorites: Verify items can be saved and retrieved later.
Shopping Cart
- Add/remove items: Test that cart updates reflect correctly.
- Quantity updates: Check recalculation of totals when quantity changes.
- Price accuracy: Validate discounts, shipping, and tax calculations.
- Persistence: Confirm cart contents remain when users refresh or log back in.
Checkout Flow
- Guest checkout: Verify checkout works without requiring account creation.
- Login during checkout: Test smooth transition for returning users.
- Address & shipping options: Ensure address validation and available shipping methods display correctly.
- Promo codes: Check valid and invalid coupons.
- Multiple payment methods: Test credit card, PayPal, gift cards, and other supported options.
- Order summary: Confirm users see accurate totals before confirming purchase.
Payments
- Valid payments: Simulate successful credit card and PayPal transactions.
- Invalid payments: Test expired cards, incorrect CVV, insufficient funds.
- Security checks: Verify sensitive data (like card details) is masked and encrypted.
- Transaction confirmation: Ensure users get confirmation on both the site and via email.
Post-Purchase
- Order confirmation email: Validate email delivery, content accuracy, and links.
- My Orders page: Check past orders are listed with correct details.
- Refunds and cancellations: Simulate canceling an order and confirm refund processing.
- Tracking: Ensure shipment tracking links work.
User Account
- Registration: Test new account creation with valid and invalid data.
- Login/logout: Verify credentials, password resets, and logout functionality.
- Profile management: Confirm users can edit address, payment methods, and preferences.
- Wishlist/favorites: Ensure saved products persist across sessions.
Non-Functional Test Cases
- Performance: Test how checkout performs under heavy load.
- Cross-browser: Verify functionality on Chrome, Firefox, Safari, Edge.
- Mobile responsiveness: Ensure mobile users can browse and purchase seamlessly.
- Accessibility: Check screen reader compatibility, alt text, keyboard navigation.
Try ecommerce web automation for free
Test easier than ever with BugBug test recorder. Faster than coding. Free forever.
Get started
Tools for E-Commerce Testing
BugBug.io
A user-friendly tool for automating web tests without coding. Ideal for testing repetitive tasks like checkout processes, it supports cloud execution for tests across various devices and browsers. Check why it's worth to choose BugBug for your business.
Selenium
The industry standard for web application testing automation, supporting all major browsers and enabling test script writing in multiple languages. It's perfect for cross-browser testing of e-commerce sites.
JMeter
An open-source tool designed for load testing and performance measurement, JMeter simulates heavy loads to test e-commerce site strength and performance during peak traffic periods.
OWASP ZAP
An open-source security tool essential for identifying vulnerabilities in web applications, ensuring e-commerce platforms are protected against potential security threats.
BrowserStack
Provides cloud-based testing across a wide range of browsers and devices, ensuring e-commerce sites offer a consistent shopping experience for all users, regardless of their device or browser.
💡 Check our curated list of the Essential Web Application Testing Tools for more effective website testing.
How to Automate E-Commerce Testing?
E-commerce websites live and die by smooth user journeys. A single broken checkout flow can mean thousands in lost sales. That’s why automating tests is no longer optional — but for many small and mid-sized teams, setting up Selenium grids or maintaining complex frameworks is overkill.
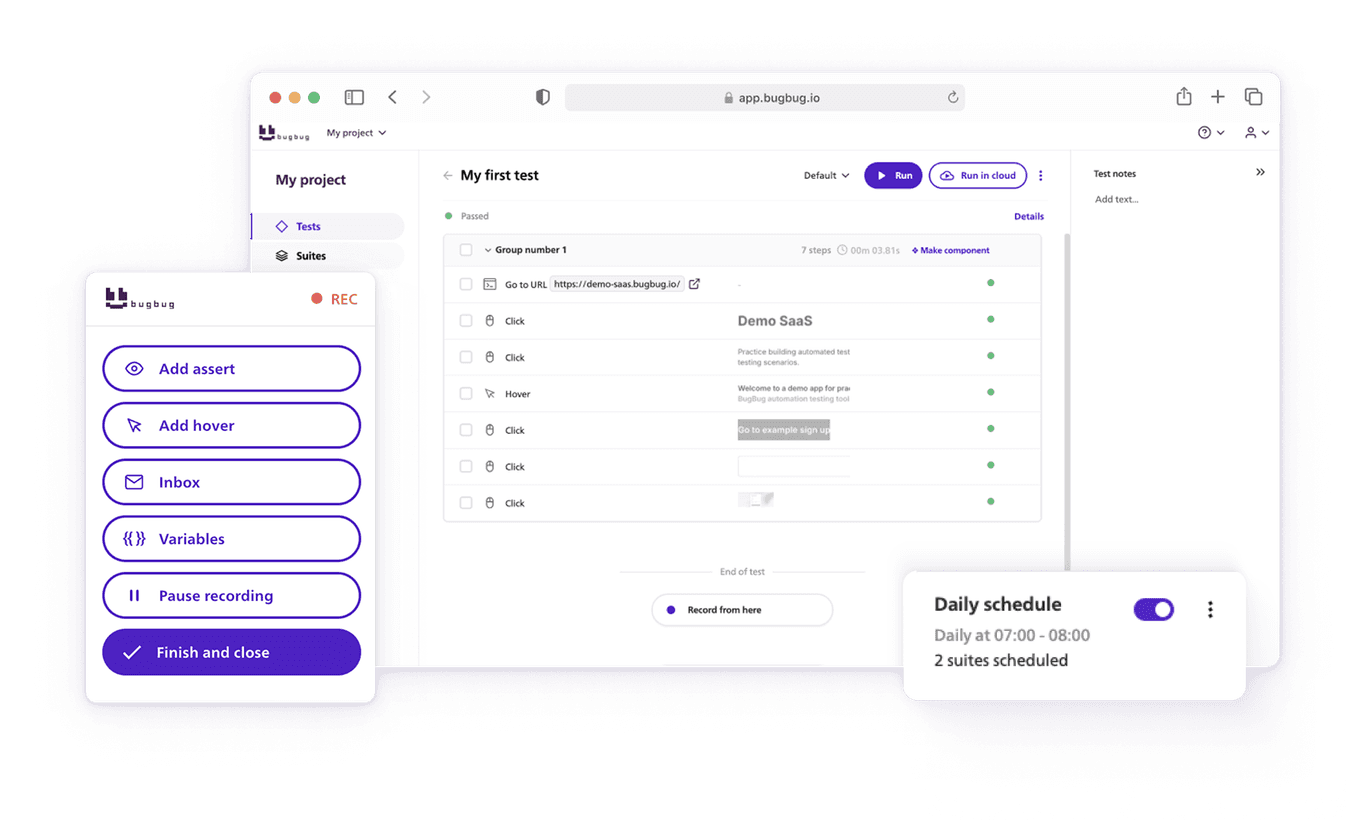
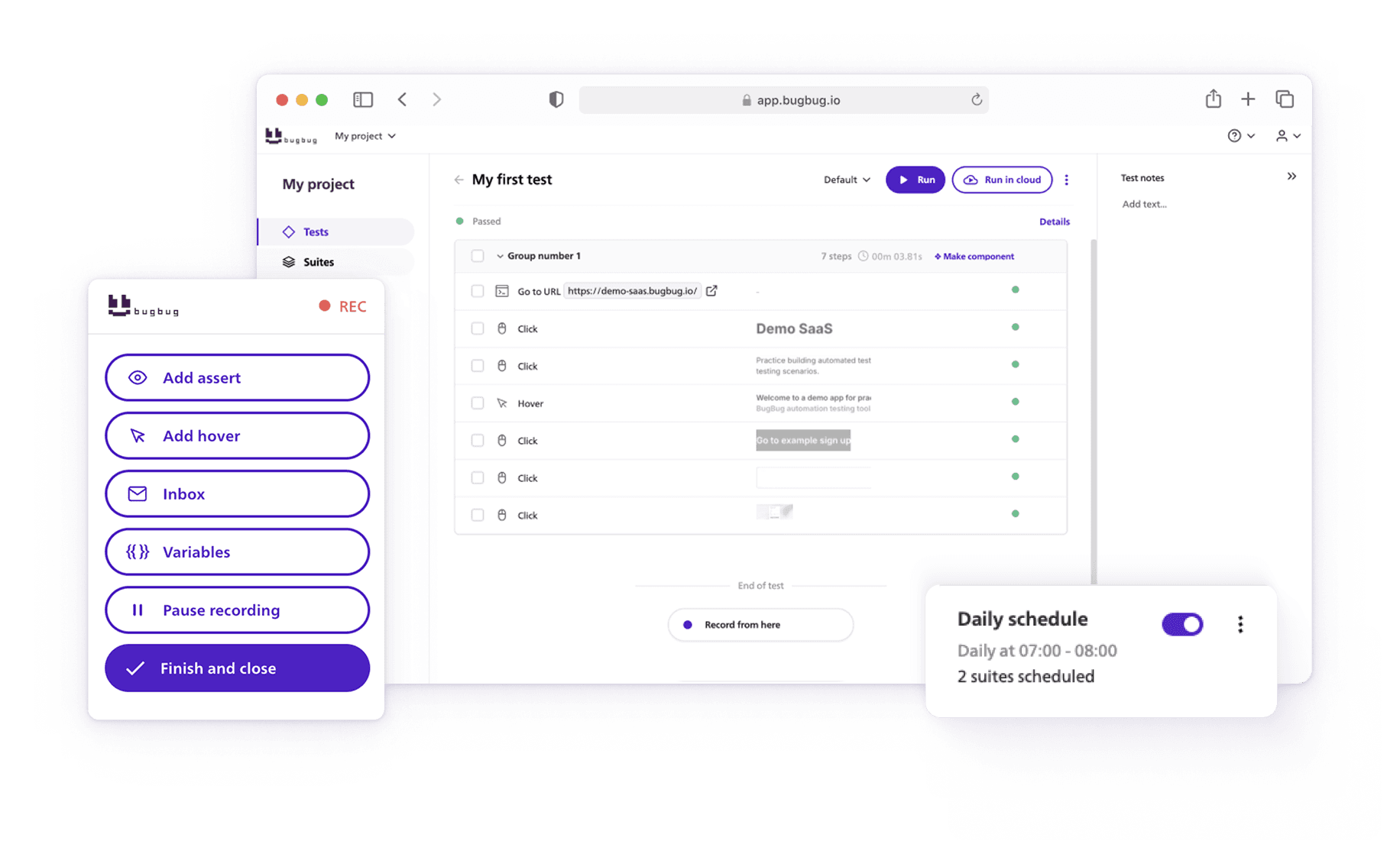
Codeless tools like BugBug offer a faster path: you can record tests directly in the browser, edit them visually, and run them locally or in the cloud without writing a single line of code.
Here’s how to get started:
Focus on Business-Critical Flows
When using a codeless tool, start by mapping the most important scenarios:
- Searching and filtering products
- Adding items to the cart
- Applying coupons and discounts
- Checkout and payment flow
- Order confirmation emails
These are your revenue-critical paths. Automating them gives the fastest ROI.
Record Your Tests
With BugBug, you simply record actions as you perform them in the browser:
- Navigate to homepage
- Type in a search query
- Add an item to cart
- Proceed to checkout
- Enter test payment data
No coding, no selectors hunting. The recorded steps mirror exactly what your users do.
Edit and Maintain with Ease
E-commerce apps change often: promotions, banners, checkout tweaks. BugBug’s Edit & Rewind feature lets you drop new steps into existing tests and restart from any point, instead of re-recording everything. This keeps your test suite lightweight and up to date.
Run Tests Automatically
Once your flows are recorded, schedule them to run:
- Locally before pushing code
- In the cloud as part of CI/CD, or at regular intervals
Automated runs ensure that every release, hotfix, or promo launch is validated instantly, without manual effort.
Cover Browsers and Devices
BugBug allows you to verify how your flows behave across browsers and devices. This matters in e-commerce, where a broken cart on Safari or a misaligned checkout on mobile can mean lost conversions.
Don’t Forget Manual Spot-Checks
Even with codeless automation, combine it with light manual testing:
- Quick usability checks on new features
- Exploratory testing during promo launches
Automation protects against regressions; manual checks catch the unexpected.
Keep Tests Aligned with Store Updates
As your e-commerce site evolves, review your tests regularly. Retire outdated scenarios, add new flows (gift cards, loyalty programs), and adapt to design changes. BugBug makes this quick, so your test suite never lags behind your product.
✅ Key takeaway: Codeless automation with BugBug makes e-commerce testing practical for lean teams. You get reliable regression coverage for checkout and other business-critical flows, without coding overhead, Selenium grids, or fragile scripts.
Conclusion
Modern e-commerce testing ensures not only functionality but also resilience. By running automated tests as part of continuous integration, teams can streamline repetitive and complicated tasks like regression testing and confirm that existing functionality is never broken by new updates. Core areas like testing product search functionality, validating payments, and protecting sensitive customer data all require thorough testing supported by modern testing techniques.
Equally important is cross device testing and browser and cross device verification, ensuring consistent performance across desktops, tablets, and smartphones. Adhering to Web Content Accessibility Guidelines makes the site inclusive, while security checks help prevent data breaches. In short, testing helps identify vulnerabilities early, safeguards trust, and leads to higher customer satisfaction by guaranteeing a positive user experience.
Done right, user experience testing in e-commerce isn’t just about bug hunting — it’s about building confidence that your platform can handle scale, adapt to change, and deliver the seamless shopping journey that today’s customers expect.
In conclusion, ecommerce site testing is a multifaceted approach to ensuring an online shopping platform is robust, secure, and provides an excellent user experience. It is an ongoing process that requires attention to detail and an understanding of the user's needs and expectations. By investing in thorough e-commerce testing, businesses can safeguard their operations, enhance customer satisfaction, and position themselves competitively in the bustling online marketplace.
Happy (automated) testing!