Software as a Service (SaaS) has revolutionized the way software development businesses operate by offering on-demand access to various applications without the need for extensive installations or hardware maintenance (it operates in cloud).
While SaaS app brings convenience and scalability, it also introduces unique challenges in terms of quality assurance. In this article we will dive deep into SaaS cloud testing, exploring its significance, various testing types, benefits, challenges, popular test solutions, and test automation process.
🎯 TL;DR - SaaS Testing Guide and Tools in 2026
- SaaS Testing Importance: Ensures cloud-based applications are functional, secure, scalable, and compatible across multiple devices and browsers.
- Key Testing Types: Includes functional, performance, security, usability, and compatibility testing to maintain reliability and a seamless user experience.
- Manual vs. Automated Testing: Manual testing is ideal for exploratory and UX testing, while automation accelerates regression and performance testing. A hybrid approach balances efficiency and flexibility.
- Challenges in SaaS Testing: Cross-browser compatibility, security concerns, continuous updates, performance bottlenecks, and integration complexities require robust testing strategies.
Best SaaS testing tools include:
-
BugBug – A codeless test automation tool for web applications with Chrome-based recording, smart wait, and CI/CD integration, ideal for teams without coding experience.
-
Selenium – A flexible, open-source tool that supports browser automation across multiple languages and frameworks, great for complex web app testing.
-
JMeter – An open-source tool focused on load and performance testing, capable of simulating heavy traffic and generating insightful performance reports.
-
Postman – A leading tool for API testing and development, offering automation, documentation, and collaboration features in a user-friendly interface.
-
Katalon Studio – A low-code automation platform supporting web, API, desktop, and mobile testing with built-in keywords and analytics for ease of use.
-
Cypress – A fast, developer-friendly JavaScript-based testing framework with real-time reloading and rich debugging tools, ideal for modern web apps.
-
SoapUI – A functional and security testing tool for REST and SOAP APIs, offering advanced features like assertions and data-driven testing.
-
TestRail – A powerful test case management platform designed for organizing, tracking, and reporting on manual and automated tests at scale.
Check also
- 🎯 TL;DR - SaaS Testing Guide and Tools in 2026
- What is SaaS Testing?
- Types of SaaS Testing Methods
- What to Choose – Manual or Automation for SaaS Application Testing?
- Manual Testing: The Human Touch
- Automation Testing: Speed and Efficiency
- The Hybrid Approach: Finding Balance
- SaaS Testing Methodology: Best Practices
- Benefits of SaaS Testing
- Criteria to Choose Saas Testing Tool
- Top Saas Testing Tools in 2025
- How to Automate SaaS Application Testing
- How to Automate SaaS Application Testing
- Saas Testing - FAQ
What is SaaS Testing?
SaaS testing is the process of evaluating Software as a Service applications to ensure and validate their functionality, performance, security, and user experience.
It involves designing and executing test cases, covering areas such as functional, usability, performance, security, and compatibility testing.
QA teams collaborate with stakeholders to identify and rectify defects, aiming to provide a seamless and reliable software experience for users. Automation is often employed to streamline app testing processes and facilitate frequent releases in SaaS environments.
Automate your tests for free
Test easier than ever with BugBug test recorder. Faster than coding. Free forever.
Sign up for free
The ultimate goal of SaaS testing is to deliver a high-quality, error-free software to customers. Unlike traditional software testing, SaaS product testing encompasses not only the application itself but also its integration with the underlying infrastructure and other connected services.
Types of SaaS Testing Methods
1. Functional Testing: This testing approach verifies whether the SaaS platform functions as intended. It involves testing individual features, user flows, and interactions to ensure that all functionalities are working correctly.
2. Performance Testing: this type of testing assesses the responsiveness, speed, scalability, and stability of the SaaS application under varying conditions. Load testing, stress testing, and scalability testing are common subtypes of performance testing.
3. Security Testing: Security is paramount in SaaS system, given the sensitive data they often handle. Security testing involves identifying vulnerabilities, ensuring data encryption, and protecting against potential threats like data breaches and unauthorized access.
4. Usability Testing: Usability testing evaluates the user-friendliness and overall user experience of the SaaS application. It involves testing navigation, accessibility, and user interface design to optimize user satisfaction.
5. Compatibility Testing: Since SaaS applications are accessed across various devices and platforms, compatibility testing checks whether the application functions correctly on different browsers, operating systems, and devices.
What to Choose – Manual or Automation for SaaS Application Testing?
The decision between manual and automated approaches for SaaS application depends on various factors.
- Manual testing is suitable for exploratory, usability, and ad-hoc testing, especially in early stages of development or for UI/UX assessment.
💡 Check also our list of the best manual testing tools.
- Automation is beneficial for repetitive tasks, enabling faster feedback in continuous deployment scenarios.
A balanced approach that combines both methods based on the specific testing needs and development cycle is often the most effective strategy.
Manual Testing: The Human Touch
Manual testing involves human testers meticulously executing test cases to identify bugs, assess user experience, and ensure the application's functionality aligns with the specifications.
This method offers several advantages, such as the ability to replicate real-world user interactions and adapt to changing requirements. Manual testers can catch nuanced issues that automated scripts might miss, making it a valuable choice for user interface (UI) testing, exploratory testing, and ad-hoc testing.
Automate your tests for free
Test easier than ever with BugBug test recorder. Faster than coding. Free forever.
Sign up for free
However, manual testing is time-consuming and labor-intensive, especially for applications with frequent updates.
💡 TIP
The repetitive nature of manual testing can also lead to human errors, and it's often challenging to simulate a large number of users and diverse scenarios manually.
Despite its limitations, manual testing's ability to assess user experience and provide qualitative feedback makes it a vital component of a comprehensive testing strategy.
Automation Testing: Speed and Efficiency
This approach employs scripts and testing tools to execute predefined test cases. It offers unmatched speed and efficiency, particularly for regression testing, load testing, and repetitive tasks.
Automated tests can be run across various platforms and configurations, making them ideal for ensuring consistent functionality across different environments.
One of the primary advantages of automated test is its ability to accelerate the testing process, providing rapid feedback and reducing time-to-market.
However, automation testing is best suited for stable functionalities and can sometimes struggle with identifying subtle UI or usability issues.
Additionally, developing and maintaining automated scripts requires specialized skills and ongoing effort, which can become an overhead in terms of time and resources.
The Hybrid Approach: Finding Balance
Many successful SaaS companies adopt a hybrid approach. This involves strategically selecting areas that benefit from automation, such as regression testing and performance testing, while reserving manual testing for aspects like user experience, exploratory testing, and edge cases.
💡 Check also our curated list of the best UI Automation Tools.
By striking a balance between the two methods, SaaS companies can harness the advantages of both. This approach leverages automation to ensure rapid feedback and efficient testing of routine scenarios, while manual testing provides the necessary human touch to uncover nuanced issues and assess the user's perspective.
SaaS Testing Methodology: Best Practices
When deciding on the testing methodology for SaaS applications, several best practices can guide SaaS companies toward making the right choice:
- Understand Application Complexity: Assess the complexity of the SaaS application, including its functionalities, integrations, and user interactions. Highly complex applications might benefit from a hybrid approach.
- Define Clear Objectives: Clearly define the testing objectives and goals. Automation can help achieve fast and repeatable results, while manual testing can provide in-depth insights into user experience.
- Prioritize Testing Types: Prioritize testing types based on critical functionalities, such as security, performance, and user interface. Automated testing can efficiently cover functional and regression tests leaving manual testing to focus on critical user journeys.
- Continuous Integration and Delivery (CI/CD): Integrate testing into the CI/CD pipeline to catch issues early in the development cycle. Check more benefits of CI/CD Pipeline Implementation
- Monitor and Evolve: Continuously monitor and assess the effectiveness of the chosen methodology. Be ready to adapt and refine the testing strategy as the application evolves and new challenges arise.
In conclusion, the decision is not a one-size-fits-all choice.
Each method has its strengths and weaknesses, and a well-informed decision should be based on the application's characteristics, testing objectives, and the desired level of quality.
💡 TIP
A hybrid approach that balances the benefits of both methods is often the most effective way to ensure a seamless user experience and robust functionality in the competitive world of SaaS.
By carefully evaluating the testing needs and adopting a comprehensive testing methodology, SaaS companies can confidently deliver high-quality applications that meet user expectations and stand out in the competitive market.
Automate your tests for free
Test easier than ever with BugBug test recorder. Faster than coding. Free forever.
Sign up for free
Benefits of SaaS Testing
1. Enhanced User Experience: Rigorous testing leads to a smoother and more reliable user experience, helping businesses retain and attract customers.
2. Reduced Downtime: Thorough testing minimizes the risk of application crashes and downtime, ensuring continuous availability for users.
3. Optimized Performance: Performance testing identifies bottlenecks and scalability issues, allowing developers to optimize the application's performance under heavy loads.
4. Data Security: Security testing ensures that user data remains secure, reducing the likelihood of data breaches and building trust with users.
5. Cost Savings: Early detection and resolution of issues through testing reduce the cost of fixing problems after deployment.
Criteria to Choose Saas Testing Tool
When selecting SaaS testing platform, it's essential to consider several critical criteria to ensure the tools meet your application's specific needs and testing challenges. Here are the key factors to consider:
- Test Automation Capability: The tool should support robust test automation to streamline repetitive testing tasks, enabling you to efficiently automate tests and enhance the overall testing process. This is crucial for continuous integration and delivery pipelines.
- Security Testing Features: Given the sensitive data handled by many SaaS applications, the tool must provide comprehensive security testing capabilities. This includes identifying vulnerabilities, ensuring data encryption, and performing penetration testing to safeguard against potential threats.
- Support for Test Cases: Effective test management is vital. The tool should allow you to create, organize, and manage test cases efficiently. It should support both manual and automated test cases to cater to different testing scenarios.
- API Testing Support: The tool must offer robust API testing capabilities since APIs are integral to SaaS applications. This includes testing RESTful and SOAP APIs for functionality, performance, and security.
- Application Testing: The tool should support various types of app testing, including web, mobile app testing, and desktop applications. It should provide a comprehensive suite of features to test the application thoroughly.
- Addressing Testing Challenges: The tool should help overcome common testing challenges such as environment setup, data management, and test coverage. It should offer features to simulate different environments and manage test data effectively.
- Regression Testing: The ability to perform regression testing efficiently is crucial. The tool should support the automation of regression tests to quickly identify any new defects introduced by changes in the application.
- Integration Testing: Ensure the tool supports integration testing to verify that different modules or services of the SaaS app work together as expected. This is particularly important for complex applications with multiple integrations.
- Software as a Service (SaaS) Model Compatibility: The tool should be designed to work seamlessly within the SaaS model, offering cloud-based solutions that align with the nature of SaaS applications.
- User Acceptance Testing (UAT): The tool should facilitate user acceptance testing to validate that the application meets the end-users' requirements and expectations. This ensures the final product is user-friendly and fit for purpose.
- Software Testing Support: Look for a tool that provides comprehensive software testing support, including functional testing, performance testing, load testing, and compatibility testing across various browsers and devices.
- Mobile App Testing: If your SaaS application includes a mobile component, the tool should offer specific features for mobile app testing to ensure optimal performance on different devices and operating systems.
By carefully evaluating these criteria, you can select the most suitable SaaS testing tools to effectively test the application, automate tests, and ensure a high-quality software product that meets user expectations and performs reliably in production environments.
Top Saas Testing Tools in 2025
BugBug: A User-Friendly Web Testing Tool

BugBug is a web application testing tool that leverages a Chrome extension to record and replay user actions. It offers features like parallel execution, suite reporting, and seamless integrations, making it ideal for startups, software agencies, and e-commerce businesses.
Automate your tests for free
Test easier than ever with BugBug test recorder. Faster than coding. Free forever.
Sign up for free
BugBug enables teams to ensure the quality of their web applications without the need for repetitive manual testing. The tool is available with a free plan that includes unlimited tests and test runs, as well as a paid plan that unlocks advanced capabilities.
Its user-friendly interface facilitates quick setup, while advanced features such as built-in variables, CI/CD integration, JavaScript actions, intelligent automation, and test scheduling cater to more complex testing needs.
Key Features:
👾 Chrome extension for recording and replaying user actions
👾 Parallel test execution and suite reporting
👾 CI/CD integration and public APIs
👾 Support for local and cloud-based test runs
👾 Test scheduling and smart waiting conditions
Strengths:
- Easy-to-use interface
- Generous free plan with essential features
- Advanced testing capabilities
- Suitable for businesses of various sizes
Best Use Cases:
- Startups and software development agencies
- E-commerce businesses
- Teams looking for efficient web app testing solutions
BugBug Example Saas App
We've just launched a Example SaaS App that you can use as a playground for creating automated tests covering core SaaS scenarios like registration processes, login, and more.
It's completely free to use, offering a perfect opportunity to experience the full potential of our testing environment and discover how BugBug can enhance your SaaS projects.
👉 Try Example SaaS App for free
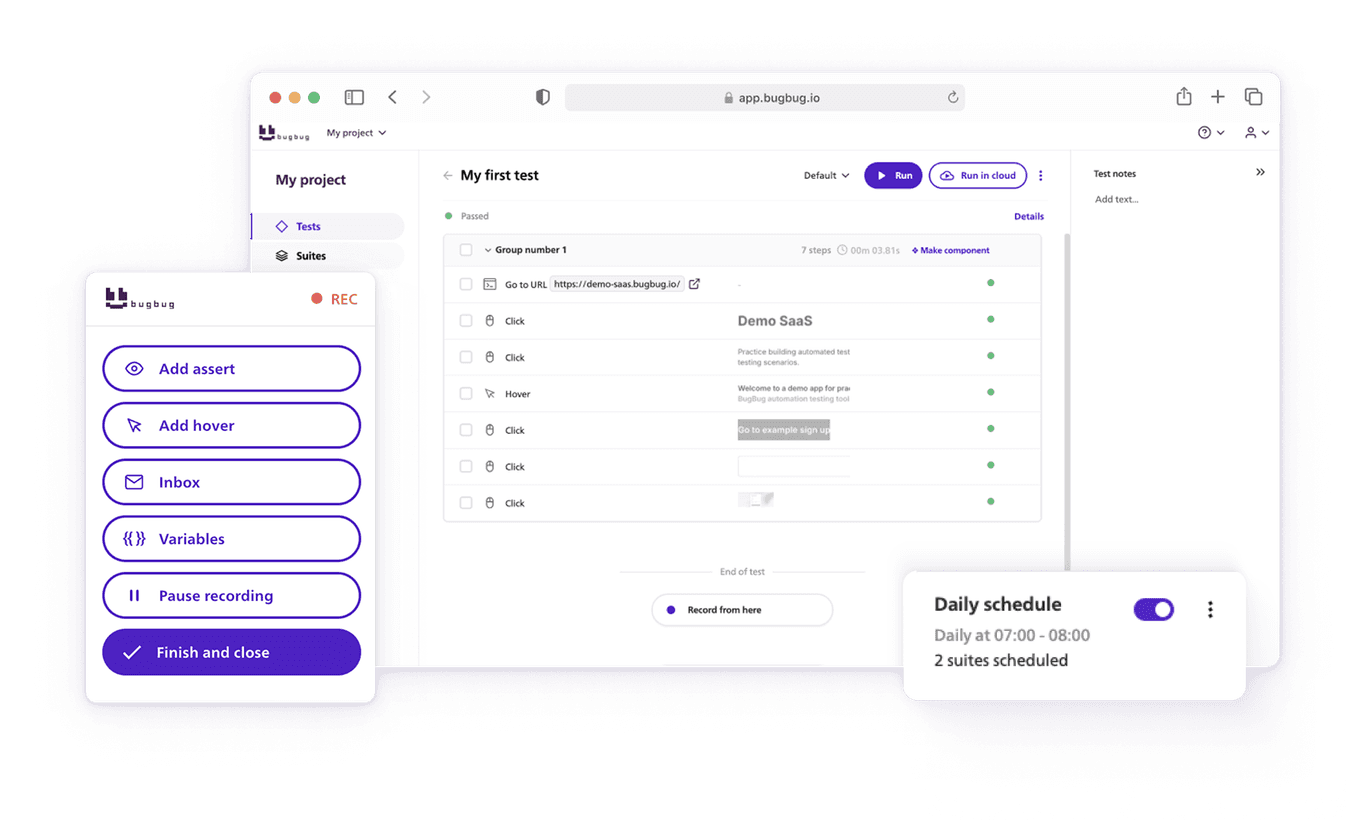
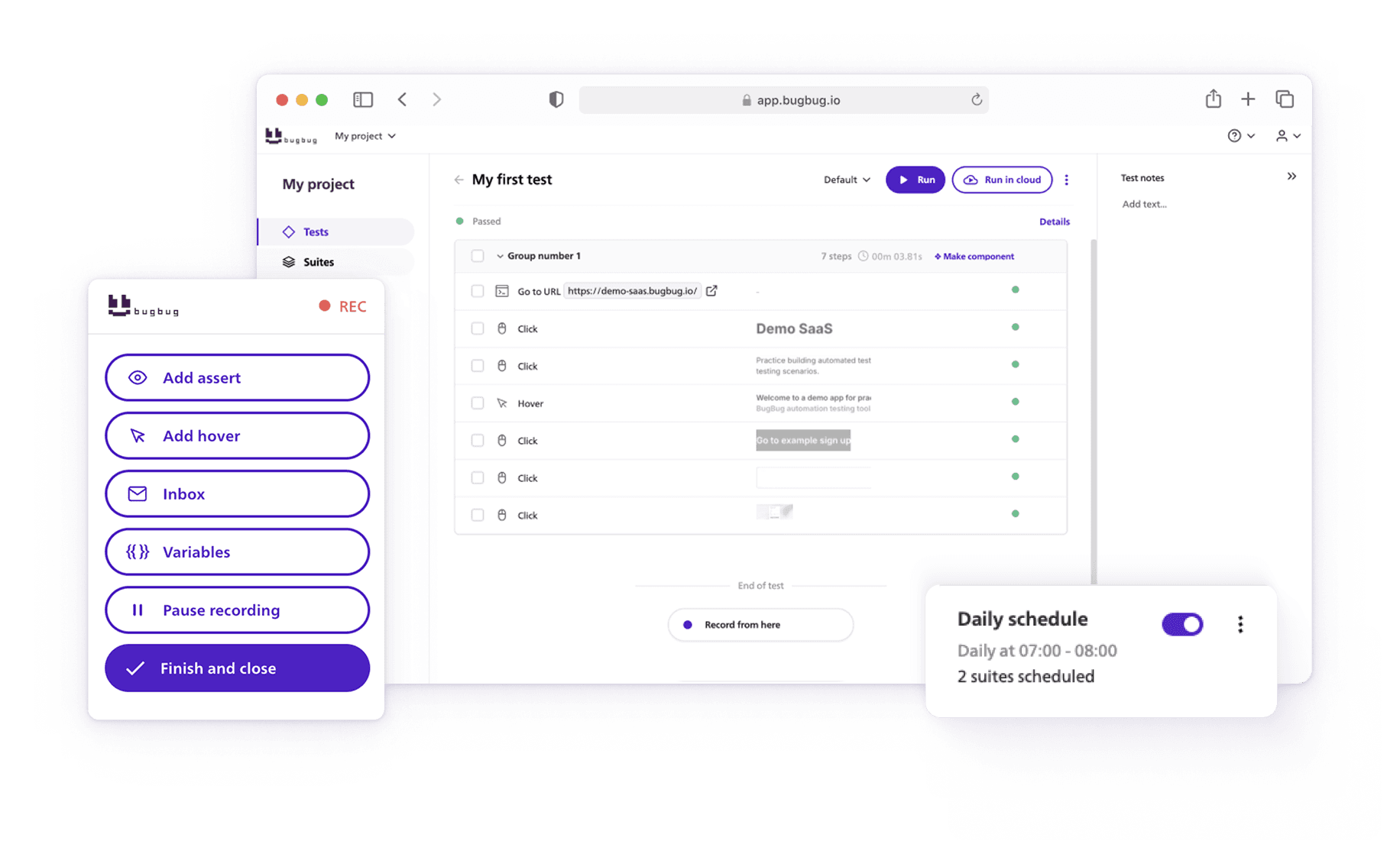
How to Test SaaS Applications in BugBug?
You can create test scenarios using a demo SaaS app to simulate user flows such as sign-up, feature usage, and logout.

Steps:
- Log into BugBug and create a new test
- Enter the URL of your SaaS app (e.g., a CRM, calendar, or todo app)
- Click “Start recording”
- Record a flow like: sign up → add a task/event → mark it done → log out
- Use BugBug’s step editor to insert validations (e.g., “Task added successfully” message)
- Click “Finish and close”
- Run the test to ensure your SaaS flow works correctly
You don't need to use recording, you can also create your tests step by step by adding particular actions and their parameters. This is however much slower!
You can manually edit steps anywhere in your test by clicking the plus symbol between the rows.

Selenium

Selenium is a widely-used open-source tool for automating web applications. It supports multiple browsers and platforms, making it a versatile choice for test automation.
Key Features:
- Supports multiple programming languages (Java, C#, Python, etc.)
- Extensive browser compatibility
- Integration with various test frameworks
- Ability to create complex and detailed test scripts
Strengths:
- Highly customizable
- Extensive community support
- Wide range of integrations
Limitations:
- Steeper learning curve for beginners
- Requires coding knowledge
Use Cases:
- Ideal for automating browser-based tests and regression testing
- Suitable for large and complex web applications
JMeter

Apache JMeter is a powerful tool for load and performance testing of web applications. It is designed to measure and analyze the performance of web applications under different load conditions.
Key Features:
- Simulates heavy load on servers, networks, or objects
- Supports various protocols (HTTP, FTP, JDBC, etc.)
- Provides extensive reporting and analysis features
- Integration with CI/CD tools
Strengths:
- Highly scalable
- Supports distributed testing
- Rich set of features for performance testing
Limitations:
- Can be resource-intensive
- Requires some level of technical expertise
Use Cases:
- Ideal for performance and load testing of web applications
- Suitable for testing the strength and scalability of servers and networks
Postman

Postman is a popular tool for API development, testing, and documentation. It provides a comprehensive suite of features for working with APIs throughout their lifecycle.
Key Features:
- Supports REST and SOAP APIs
- Automated testing with the collection runner
- Easy-to-use interface for creating and managing API requests
- Integration with CI/CD pipelines
Strengths:
- User-friendly interface
- Extensive API testing capabilities
- Excellent for API development and documentation
Limitations:
- Limited support for non-API testing
- Some advanced features require a paid subscription
Use Cases:
- Best for comprehensive API testing and development
- Suitable for teams focusing on API lifecycle management
Katalon Studio

Katalon Studio is an all-in-one test automation tool for web, API, mobile, and desktop applications. It offers a wide range of testing capabilities, including functional, regression, and API testing.
Key Features:
- Supports multiple platforms (web, mobile, desktop)
- Built-in keywords for creating tests without coding
- Integration with CI/CD tools
- Detailed reporting and analytics
Strengths:
- All-in-one solution
- User-friendly for both beginners and experienced testers
- Extensive integrations and built-in features
Limitations:
- Can be resource-intensive
- Some features require a paid subscription
Use Cases:
- Suitable for teams looking for an all-in-one test automation solution
- Ideal for projects that require testing across multiple platforms
Automate your tests for free
Test easier than ever with BugBug test recorder. Faster than coding. Free forever.
Sign up for free
Cypress

Cypress is a modern end-to-end testing tool designed for developers. It provides a fast, reliable, and developer-friendly testing experience for web applications.
Key Features:
- Real-time reloads and automatic waiting
- Network traffic control and mocking
- Detailed and interactive test runner
- Supports JavaScript-based test scripting
Strengths:
- Developer-friendly
- Fast test execution
- Excellent debugging capabilities
Limitations:
- Limited support for cross-browser testing
- Primarily focused on JavaScript
Use Cases:
- Ideal for front-end developers and end-to-end testing of web applications
- Suitable for modern web applications built with JavaScript frameworks
SoapUI

SoapUI is a popular tool for functional and security testing of APIs. It supports both REST and SOAP protocols and provides powerful data-driven testing capabilities.
Key Features:
- Supports REST and SOAP APIs
- Data-driven testing and assertions
- Integration with various CI/CD tools
- Advanced security testing features
Strengths:
- Comprehensive API testing capabilities
- Supports complex test scenarios
- Strong security testing features
Limitations:
- Steeper learning curve for beginners
- May require a paid subscription for advanced features
Use Cases:
- Best for functional testing of web services
- Suitable for teams focusing on API security testing
TestRail
TestRail is a comprehensive test case management tool that helps teams organize, manage, and track their testing efforts. It provides detailed reporting and analytics to improve test coverage and efficiency.
Key Features:
- Test case creation and management
- Detailed reporting and analytics
- Integration with various test automation tools
- Customizable workflows and fields
Strengths:
- Excellent test management capabilities
- Detailed and customizable reporting
- Strong integration options
Limitations:
- Can be expensive for large teams
- May require some configuration and setup
Use Cases:
- Ideal for teams looking for effective test management and reporting
- Suitable for large projects with complex test management needs
QTest

QTest by Tricentis offers robust test management capabilities and integrates well with various automation tools and CI/CD pipelines. It is designed for enterprise-level test management and collaboration.
Key Features:
- Test case management and execution
- Integration with automation tools and CI/CD pipelines
- Real-time reporting and dashboards
- Collaboration features for team management
Strengths:
- Enterprise-level capabilities
- Strong integration and collaboration features
- Real-time reporting and analytics
Limitations:
- Can be expensive for small teams
- Requires some configuration and setup
Use Cases:
- Suitable for enterprise-level test management
- Ideal for large teams requiring robust collaboration and reporting features
Automate your tests for free
Test easier than ever with BugBug test recorder. Faster than coding. Free forever.
Sign up for free
Appium

Appium is widely used for automating mobile app testing. It supports cross-platform testing for both iOS and Android applications, allowing for the automation of native, hybrid, and mobile web apps.
Key Features:
- Supports multiple platforms (iOS, Android)
- Integration with various test frameworks
- Ability to write tests in multiple programming languages
- Cross-platform test automation
Strengths:
- Strong support for mobile app testing
- Cross-platform capabilities
- Extensive community support
Limitations:
- Can be complex to set up
- May require specific hardware for testing
Use Cases:
- Best for mobile app test automation
- Suitable for projects requiring cross-platform mobile testing
LoadRunner

LoadRunner by Micro Focus is a leading performance testing tool. It allows testing various applications, measuring system behavior, and performance under load.
Key Features:
- Supports multiple protocols (HTTP, FTP, etc.)
- Extensive reporting and analysis features
- Ability to simulate thousands of users
- Integration with CI/CD tools
Strengths:
- Highly scalable
- Comprehensive performance testing capabilities
- Strong reporting and analysis
Limitations:
- Can be expensive
- Requires technical expertise
Use Cases:
- Ideal for enterprise-grade load and performance testing
- Suitable for large-scale applications and systems
BrowserStack
BrowserStack allows for testing web applications across various browsers and devices. It provides a real device cloud for manual and automated testing.
Key Features:
- Real device cloud for testing
- Supports manual and automated testing
- Cross-browser and cross-device compatibility
- Integration with CI/CD tools
Strengths:
- Excellent for compatibility testing
- Wide range of devices and browsers
- Easy integration with automation tools
Limitations:
- Can be expensive for extensive testing needs
- May have performance limitations for large-scale tests
Use Cases:
- Best for compatibility testing across multiple browsers and devices
- Suitable for ensuring cross-browser functionality
How to Automate SaaS Application Testing
Testing SaaS applications presents a notable challenge for SaaS companies, primarily due to the limited control over user devices. The applications are accessed from various browsers and devices, which makes Cross browser testing imperative.
BugBug gives you the opportunity to create different end-to-end test cases. Testing starts from a clean slate by using incognito mode to avoid any pre-existing cookies or cache. Clicks and typing are recorded, the tool records every click. BugBug covers all the basic flow of the testing process. You can easily create, run, edit and maintain the growing number and complexity of your tests.
Automate your tests for free
Test easier than ever with BugBug test recorder. Faster than coding. Free forever.
Sign up for free
How to Automate SaaS Application Testing
Testing SaaS applications presents a notable challenge for SaaS companies, primarily due to the limited control over user devices. The applications are accessed from various browsers and devices, which makes Cross browser testing imperative.
BugBug gives you the opportunity to create different end-to-end test cases. Testing starts from a clean slate by using incognito mode to avoid any pre-existing cookies or cache. Clicks and typing are recorded, the tool records every click. BugBug covers all the basic flow of the testing process. You can easily create, run, edit and maintain the growing number and complexity of your tests.
There are many Saas Testing challenges. SaaS testers need to test the application in various environments and configurations to ensure compatibility and performance. Security of SaaS applications is another major concern, requiring dedicated security testing solutions to protect sensitive data. SaaS testing tools help address these challenges by providing automated, efficient, and comprehensive testing solutions.
In summary, testing a saas application is a process that involves various testing types and strategies to ensure that SaaS applications are functional, performant, and secure. SaaS testing tools are essential for automating and streamlining testing activities, helping SaaS companies deliver high-quality products.
By following best practices for SaaS application testing and using a combination of automated and manual testing methods, organizations can ensure that their SaaS products meet the highest standards of quality and reliability.
Saas Testing - FAQ
What are the best functional testing tools?
Top functional testing tools include:
- BugBug – Codeless test automation for web applications.
- Selenium – Open-source automation for functional web testing.
- TestComplete – Functional UI and API testing.
- Katalon Studio – No-code functional testing across platforms.
- Ranorex – GUI and functional testing for desktop, mobile, and web applications.