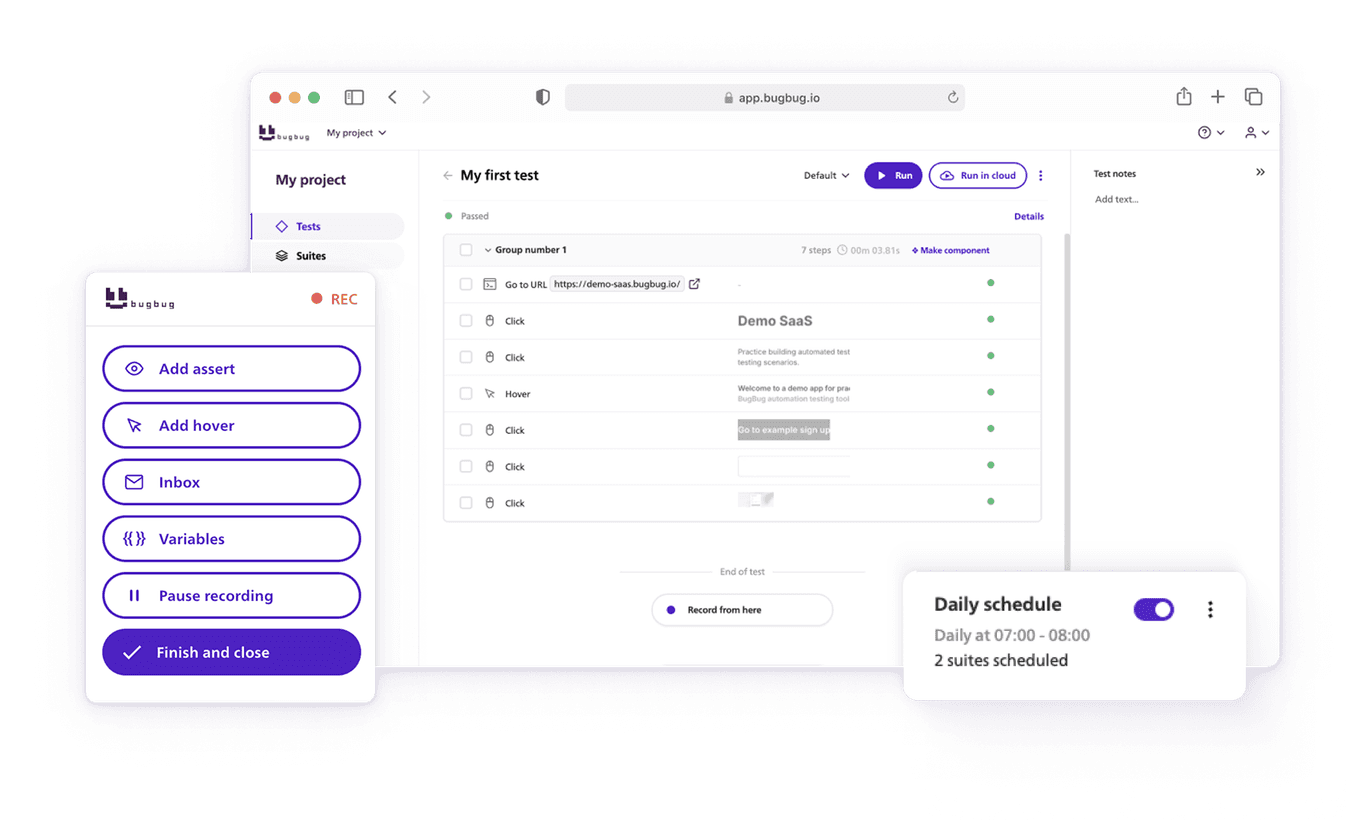
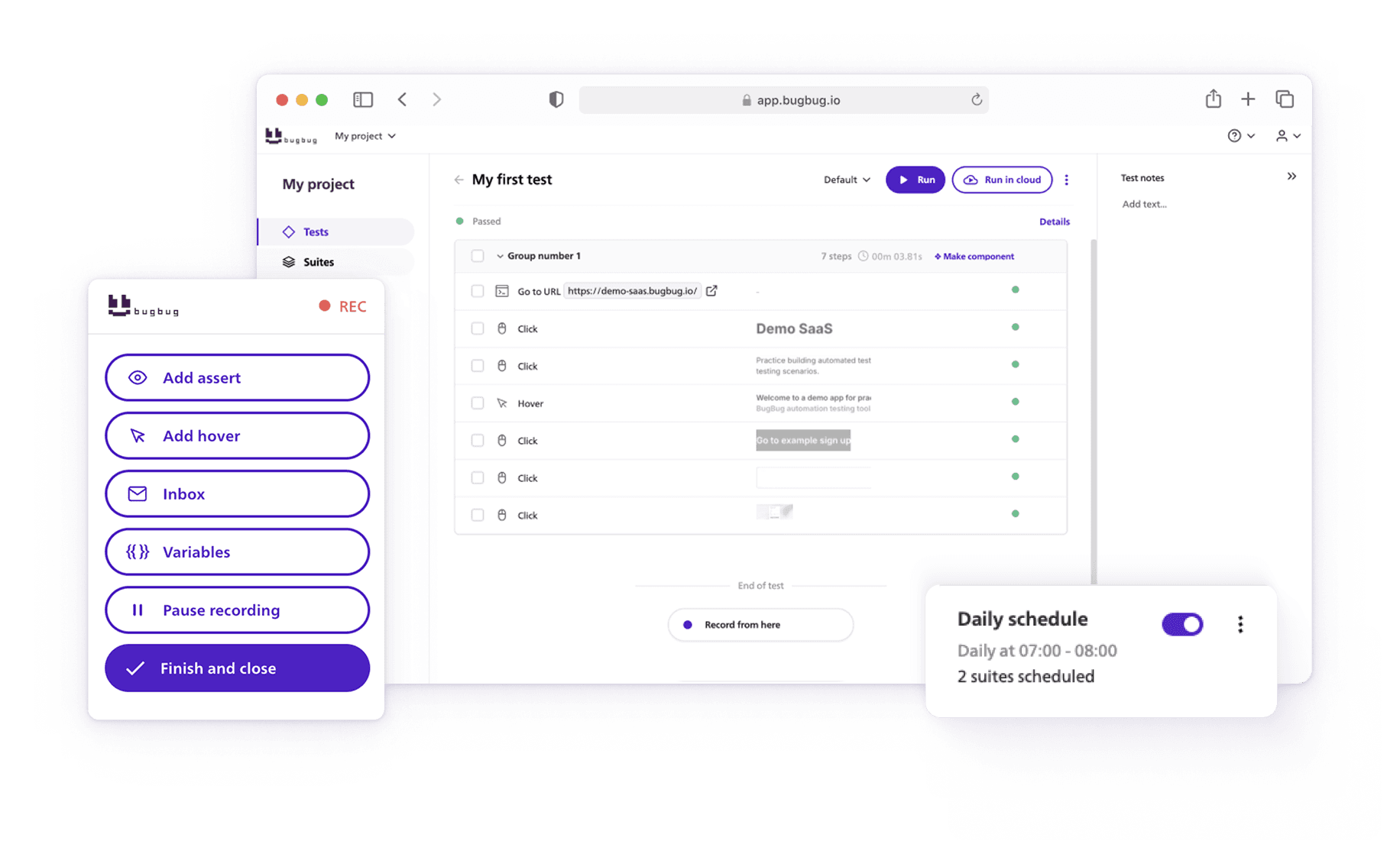
Front-end testing is a software testing process that focuses on evaluating UI and user experience (UX) of a web application, mobile app, or any software with a graphical user interface (GUI).
The primary goal of front-end testing is to ensure that the application's front-end components, including the visual elements, interactions, and functionalities, work as intended and provide a seamless and user-friendly experience.
TL;DR
- This blog post aims to delve deep into the intricacies of front-end testing frameworks, charting their significance, evolution, and application in the current digital era.
- We offer a holistic view of the front-end testing landscape by interweaving theoretical insights with practical examples and expert opinions.
Check also:
- The Ultimate XPath Cheat Sheet
- Testing Tools for Web Application
- Ultimate Guide to Test Automation Frameworks
- TL;DR
- Key Aspects of Front-End Testing
- Why Front End Testing?
- Front End Testing vs End-to-End Testing
- Benefits of Front End Testing
- Types of Front End Testing
- Devising a Front End Testing Plan
- Challenges of Front End Testing
- Spotlight on JavaScript Front End Testing Frameworks
- Top 10 Front End Testing Frameworks of 2024
- FAQ Section

Automate your tests for free
Test easier than ever with BugBug test recorder. Faster than coding. Free forever.
Get started
Key Aspects of Front-End Testing
Functionality Testing
This involves checking that the interactive elements such as buttons, links, forms, and navigation work correctly. Testers ensure that user interactions produce the expected outcomes.
Cross-Browser Compatibility
Front-end tests ensure that the application appears and functions consistently across different web browsers like Chrome, Firefox, Safari, and Edge.
Responsive Design Testing
Testing for responsiveness involves checking how the application adapts to various screen sizes and orientations (e.g., mobile, tablet, desktop). It ensures that the UI remains user-friendly on different devices.
Performance Testing
This aspect checks the speed and efficiency of the front-end components. It includes evaluating page load times, resource usage, and overall performance under different conditions.
Usability Testing
Usability tests focus on user experience and design aspects. Testers evaluate whether the application is intuitive, easy to navigate, and visually appealing.
Accessibility Testing
This type of testing ensures that the application is accessible to people with disabilities. It involves checking compliance with accessibility standards such as WCAG (Web Content Accessibility Guidelines).
Security Testing
Front-end security testing involves identifying and mitigating vulnerabilities in the UI layer that could be exploited by malicious actors, such as cross-site scripting (XSS) or cross-site request forgery (CSRF).
Regression Testing
What is Regression Testing? Regression testing is a software testing method that aims to investigate and locate any possible flaws or bugs in software that has already been fully developed.
Front-end testing can be automated using various testing frameworks and tools, such as Selenium, Cypress, Puppeteer, and many others.
Test automation helps ensure consistent and repeatable testing procedures, especially when there are frequent changes or updates to the application.
Automate your tests for free
Test easier than ever with BugBug test recorder. Faster than coding. Free forever.
Get started
Why Front End Testing?
The front end is the interface between users and your digital product. A flawless front end experience boosts user satisfaction, driving both engagement and conversions. This makes front end testing indispensable for ensuring a superior user experience and seamless interface functionality.
Front End Testing vs End-to-End Testing
The main goal of front-end testing is to ensure that the application's UI and user interactions work as intended. This includes verifying that the UI is responsive, consistent, user-friendly, and free from bugs or issues that may affect the user experience.
End-to-end testing, on the other hand, looks at the entire application from start to finish. It involves testing the full user journey, often spanning multiple components, layers, and systems of the application. This includes not only the front-end but also the back-end, APIs, and any external integrations.
End-to-end testing can involve various types of web app testing, including integration testing (to check the interactions between different components), API testing (to ensure that APIs work as expected), and user journey testing (to test the entire process a user goes through). While it encompasses front-end testing, it goes beyond the UI to validate the complete functionality of the application.
End-to-end testing platforms and frameworks often simulate user interactions with the application and can include both front-end and back-end components. Tools like BugBug Protractor, Nightwatch, and Playwright are commonly used for E2E testing.
Automate your tests for free
Test easier than ever with BugBug test recorder. Faster than coding. Free forever.
Get started
Benefits of Front End Testing
Front-end testing offers several benefits to both developers and end-users, contributing to the overall success and quality of a software application.
Some of the key advantages of front-end testing include:
- Improved User Experience: Front-end testing helps identify and fix user interface issues, ensuring that the application is user-friendly, intuitive, and responsive. This leads to a positive user experience, which is crucial for user satisfaction and retention.
- Early Bug Detection: By catching UI and functionality issues at an early stage, front-end testing reduces the cost and effort required to fix defects. It contributes to a smoother development process and faster release cycles.
- Consistency Across Platforms: Front-end tests ensure that the application functions consistently on different browsers, devices, and screen sizes. This consistency is vital for reaching a broader audience and reducing user frustration.
- Accessibility Compliance: Testing for accessibility helps make the application usable for individuals with disabilities. Ensuring compliance with accessibility standards not only broadens the user base but also helps meet legal and ethical obligations.
- Faster Development: Automated front-end testing frameworks and tools can speed up the testing process, allowing developers to release features and updates more quickly. Automation also reduces the risk of human error in testing.
- Enhanced Security: Front-end testing can identify vulnerabilities in the UI layer, helping to prevent security threats such as cross-site scripting (XSS) and cross-site request forgery (CSRF). This enhances the overall security of the application.
- Optimized Performance: Performance testing can uncover performance bottlenecks, slow-loading pages, or resource-intensive UI components. Addressing these issues improves the application's speed and responsiveness, which is crucial for user satisfaction.
- Regulation and Compliance: Front-end testing can ensure that the application adheres to industry-specific regulations and compliance standards, which is essential for applications in sectors like healthcare, finance, and e-commerce.
- Reduced Support and Maintenance Costs: Fewer UI-related issues mean a lower number of support tickets and less time spent on maintenance. This results in cost savings for the development team.
- Competitive Advantage: Applications that consistently provide a high-quality front-end experience gain a competitive edge in the market. Users are more likely to choose and stick with applications that are easy to use and bug-free.
- User Trust: Reliable front-end performance and functionality build trust with users. They are more likely to trust and engage with an application that doesn't present frequent UI problems or errors.
- Enhanced Collaboration: Front-end testing encourages collaboration between development and quality assurance (QA) teams. It fosters communication and mutual understanding of the application's requirements and expectations.
Automate your tests for free
Test easier than ever with BugBug test recorder. Faster than coding. Free forever.
Get started
Types of Front End Testing
Front-end testing encompasses various types of testing, including functional testing, integration testing, cross-browser compatibility testing, responsive design testing, usability testing, accessibility testing, performance testing, and security testing. These tests focus on the presentation layer and how users interact with the application.
What Aspects to Test in the Front End?
Key aspects to test include:
- User Interface (UI): This involves ensuring visual consistency across different screens and verifying that the design matches the mockups or wireframes. Elements like colors, fonts, spacing, and positioning are checked for alignment with the design guidelines.
- Functionality: This aspect covers testing of buttons, forms, links, and other interactive elements. Testers ensure that these elements work as expected and that user interactions produce the desired outcomes.
- Performance: Here, testers assess the load times of pages, how quickly interactive elements respond to user actions, and whether any components cause lag or delay in the user experience.
- Compatibility: This involves ensuring that the application functions as intended on different browsers, devices, and screen sizes. It's vital to verify that the application offers a consistent experience across all supported platforms.
- Usability: This aspect focuses on the user experience, assessing whether the application is intuitive, easy to navigate, and meets user expectations. Factors like content readability, navigation flow, and error messages are evaluated.
- Accessibility: Testing for accessibility ensures that the application can be used by individuals with disabilities. This includes checking for keyboard navigation, screen reader compatibility, and adherence to accessibility guidelines like WCAG.
- Security: In the context of front-end testing, security involves checking for vulnerabilities in the UI layer. Testers look for issues like cross-site scripting (XSS) vulnerabilities, insecure data storage, or potential breaches of user privacy.
Devising a Front End Testing Plan
Devising a front-end testing plan is essential to ensure the quality and reliability of your application's user interface and user experience. A well-structured testing plan helps identify potential issues early in the development process and provides a roadmap for conducting front-end testing.
Check also:
- Test Planning: Create a Test Plan for Your Business
- Test Plan vs Test Strategy: Goals & Differences
- Automation Test Plan Template
Here's a step-by-step guide to creating a front-end testing plan:
Understand the Requirements
Start by understanding the requirements of the application. This includes both functional requirements (what the application should do) and non-functional requirements (how the application should perform).
Define Test Objectives
Based on the requirements, define clear test objectives. These objectives should state what you intend to achieve with the testing process. For instance, one objective might be to verify that the application's navigation bar works consistently on all supported browsers.
Select Testing Tools
Choose the appropriate tools and frameworks for front-end testing. Depending on the scope and nature of your application, you might need tools for automated testing, cross-browser testing, performance testing, and more.
Design Test Cases
Design detailed test cases that outline the specific actions to be performed, the expected outcomes, and the criteria for success. For example, a test case might involve checking the functionality of a login form, ensuring that it provides an error message when incorrect credentials are entered.
Execute the Tests
Execute the test cases, either manually or using automated testing tools. As you conduct the tests, document any issues or discrepancies you encounter.
Analyze Test Results
Once testing is complete, analyze the results. Identify any patterns in the issues found, prioritize them based on their severity and impact, and communicate your findings to the development team.
Review and Iterate
After the issues have been addressed, re-test the application to ensure that the fixes have been implemented correctly. Continue this iterative process of testing, reviewing, and refining until the application meets the desired quality standards.
Post-Release Monitoring
Consider implementing ongoing monitoring and testing of the application in the production environment to catch any issues that may arise after release.
Automate your tests for free
Test easier than ever with BugBug test recorder. Faster than coding. Free forever.
Get started
Challenges of Front End Testing
Front-end testing can be a crucial part of ensuring a positive user experience and the overall quality of a software application. However, it comes with its set of challenges that testers and developers need to address. Some of the common challenges of front-end testing include:
- Cross-Browser Compatibility: Web applications must work consistently across various web browsers (e.g., Chrome, Firefox, Safari, Edge), each with its quirks and rendering engines. Testing and ensuring compatibility across all these browsers can be time-consuming and challenging.
- Responsive Design Testing: Ensuring that an application looks and functions correctly on different screen sizes and resolutions, including mobile devices, tablets, and desktops, can be complex. Responsive design testing is vital but can be resource-intensive.
- Usability Testing: Evaluating the user interface for usability and user-friendliness requires subjective judgment and can be challenging to quantify. Testers must understand user expectations and preferences.
- Accessibility Testing: Ensuring that the application is accessible to individuals with disabilities involves adherence to accessibility guidelines (e.g., WCAG). This can be intricate and requires specialized knowledge and tools.
- Performance Testing: Identifying and resolving performance issues, such as slow page load times, inefficient code, or unoptimized assets, can be challenging. Performance testing requires a thorough understanding of the application's architecture and dependencies.
- Dynamic Content and Interactivity: Modern web applications often rely heavily on JavaScript and dynamic content. Testing the interactivity and functionality of these dynamic components can be complex, especially when using different frameworks and libraries.
- Test Data Management: Managing test data for front-end testing, especially in complex scenarios, can be difficult. It may involve creating and maintaining test databases or API mocks to simulate various data inputs.
Automate your tests for free
Test easier than ever with BugBug test recorder. Faster than coding. Free forever.
Get started
Spotlight on JavaScript Front End Testing Frameworks
JavaScript is the language that powers much of the web. It's the driving force behind dynamic and interactive web applications, including those built with popular libraries and frameworks like React. JavaScript testing frameworks play a vital role in ensuring the quality and reliability of web applications, particularly when it comes to the user interface.
Automate your tests for free
Test easier than ever with BugBug test recorder. Faster than coding. Free forever.
Get started
Top 10 Front End Testing Frameworks of 2024
To aid you in your testing journey, here's a list of tools for automated front-end testing in 2023, complete with their features, advantages, disadvantages, and user feedback:
Selenium

Selenium is a widely recognized open-source test automation framework that allows developers and testers to automate web browsers. It is primarily used for automating web applications for testing purposes but can also be used to automate other browser-based tasks.
Key Features:
- Supports multiple programming languages (Java, Python, C#, Ruby, etc.).
- Capable of running tests across different web browsers (Chrome, Firefox, Safari, etc.).
- Supports parallel test execution and integration with CI/CD pipelines.
- Extensive support for various operating systems.
Strengths:
- Highly flexible and extensible.
- Extensive community support and a rich ecosystem of plugins and integrations.
- Strong cross-browser testing capabilities.
- Well-suited for complex web applications.
Limitations:
- Steeper learning curve compared to some newer tools.
- Requires external test runners and additional configuration.
- May encounter issues with dynamic content and timing.
Best Use Cases:
- Cross-browser testing of web applications.
- Automating repetitive tasks in web applications.
- Large-scale test automation projects requiring extensive customizability.
Check also Best Selenium Practice Websites
Cypress
Cypress is a modern web automation testing tool designed to simplify end-to-end testing of web applications. It is known for its fast execution, real-time reloads, and ability to interact directly with the browser’s DOM.
Key Features:
- Real-time reloads with immediate display of test results.
- Direct access to the browser's DOM for more reliable tests.
- Built-in test runner and assertion library.
- Simple, intuitive syntax and architecture.
- Built-in support for mocking and stubbing.
Strengths:
- Fast and reliable due to direct browser interactions.
- Excellent for testing modern JavaScript frameworks like React, Angular, and Vue.
- Great developer experience with interactive test runner.
- Comprehensive documentation and strong community support.
Limitations:
- Limited support for cross-browser testing (primarily supports Chrome and Firefox).
- Not suitable for testing non-web-based applications.
- Requires running within the Node.js environment.
Best Use Cases:
- End-to-end testing of modern web applications.
- Testing single-page applications (SPAs) built with JavaScript frameworks.
- Continuous integration pipelines requiring fast and reliable feedback.
Check also Cypress Best Practices
Jest

Jest is a zero-config testing framework developed by Facebook, primarily for testing JavaScript applications, including those built with React. It is known for its simplicity, speed, and powerful features like mocking and snapshot testing.
Key Features:
- Built-in support for mocking, spies, and stubs.
- Snapshot testing for UI components.
- Parallel test execution for faster test runs.
- Integrated code coverage reports.
- No configuration needed for most JavaScript projects.
Strengths:
- Easy to set up and use, especially in React projects.
- Fast execution with built-in parallel testing.
- Comprehensive and detailed error messages.
- Strong ecosystem with many plugins and integrations.
Limitations:
- Primarily focused on JavaScript, limiting its use with non-JS languages.
- May require additional configuration for complex testing scenarios.
- Less suited for cross-browser testing.
Best Use Cases:
- Unit and integration testing for JavaScript/TypeScript applications.
- Testing React components with snapshot testing.
- Projects requiring quick setup and minimal configuration.
Puppeteer

Puppeteer is an official tool from Google that provides a high-level API to control headless Chrome or Chromium browsers via Node.js. It is commonly used for automating browser tasks, such as taking screenshots, generating PDFs, and performing web scraping.
Check how does Puppeteer Recorder compare to BugBug.
Key Features:
- Controls headless Chrome/Chromium for automation.
- Can perform tasks like rendering, screenshot capture, and PDF generation.
- Supports automating user interactions such as clicks and form submissions.
- Provides performance metrics and debugging capabilities.
Strengths:
- Direct control over Chrome/Chromium browsers.
- Excellent for tasks beyond testing, such as web scraping and performance monitoring.
- Headless mode allows for fast and efficient execution.
- Strong support for modern web standards.
Limitations:
- Limited to Chrome/Chromium browsers, restricting cross-browser testing.
- Requires familiarity with Node.js.
- Less suited for high-level testing scenarios compared to tools like Selenium.
Best Use Cases:
- Web scraping and data extraction from websites.
- Generating screenshots and PDFs from web pages.
- Performance monitoring and automation of web-based tasks.
Playwright

Playwright is a newer web automation tool developed by Microsoft, designed for testing across multiple browsers, including Chrome, Firefox, Safari, and Edge. It is known for its robust automation features like auto-wait, network interception, and tracing. Check our Playwright Cheat Sheet to get you started with the framework.
Key Features:
- Supports multiple browsers, including non-Chromium-based ones.
- Auto-wait feature for handling elements and actions.
- Network interception and request mocking.
- Multi-page and multi-domain testing.
- Detailed tracing and debugging tools.
Strengths:
- Cross-browser testing with a single API.
- Reliable and stable due to auto-wait and network interception features.
- Excellent for debugging with detailed traces and logs.
- Active development and strong support from Microsoft.
Limitations:
- Relatively new, with a smaller community compared to Selenium.
- Requires a good understanding of asynchronous programming.
- May have compatibility issues with legacy systems.
Best Use Cases:
- Cross-browser testing across different browser engines.
- Automating complex testing scenarios with multi-page interactions.
- Testing modern web applications with robust debugging requirements.
TestCafe

TestCafe is a Node.js-based framework for testing web applications. It is unique in that it does not rely on WebDriver or browser plugins, making it easier to set up and use. TestCafe can run tests in multiple browsers simultaneously, both locally and in the cloud.
Key Features:
- Does not require WebDriver or browser plugins.
- Runs tests across different browsers simultaneously.
- Built-in support for running tests in headless mode.
- Supports JavaScript and TypeScript out of the box.
- Integrated test runner with live test monitoring.
Strengths:
- Simple setup with no need for additional browser drivers or plugins.
- Runs on any browser that supports HTML5.
- Good support for parallel testing and CI/CD integration.
- Strong documentation and active community.
Limitations:
- Limited ecosystem compared to more established tools like Selenium.
- Performance may not match that of more lightweight tools for very large test suites.
- Fewer integrations with non-JavaScript technologies.
Best Use Cases:
- End-to-end testing for JavaScript and TypeScript applications.
- Teams looking for a simple, all-in-one testing tool.
- Projects needing cross-browser testing without complex setup.
Webdriver.io

WebdriverIO is a JavaScript-based testing framework that provides a custom implementation of WebDriver's bindings. It is designed to work seamlessly with modern web frameworks and technologies, making it a powerful tool for end-to-end testing.
Key Features:
- Custom implementation of WebDriver for enhanced flexibility.
- Integrates well with popular frameworks like React, Angular, and Vue.
- Supports BDD and TDD testing styles.
- Built-in parallel test execution and CI/CD support.
- Wide range of plugins and integrations available.
Strengths:
- Flexible and extensible with a robust plugin system.
- Works well with modern JavaScript frameworks and technologies.
- Supports advanced testing scenarios, including visual regression and performance testing.
- Strong community support and frequent updates.
Limitations:
- Requires a good understanding of WebDriver and JavaScript.
- Initial setup can be complex for beginners.
- Performance may vary depending on the complexity of the test cases.
Best Use Cases:
- End-to-end testing of modern web applications.
- Integration with BDD frameworks like Cucumber.
- Projects requiring extensive customization and flexibility in test automation.
Automate your tests for free
Test easier than ever with BugBug test recorder. Faster than coding. Free forever.
Get started
FAQ Section
What is front-end testing?
A: Front-end testing is a type of testing that focuses on checking the functionality and user interface of a website or application. It involves automating tests to ensure that all elements, such as buttons, forms, and layouts, work correctly.
Why is cross-browser testing important?
A: Cross-browser testing ensures that a website or application works correctly across different browsers, taking into account their unique quirks and rendering engines. This ensures a consistent user experience regardless of the browser choice.
What is responsive design testing?
A: Responsive design testing ensures that a website or application adjusts correctly based on the device's screen size, ensuring an optimal user experience on mobile devices, tablets, and desktops.
How do I choose the right testing framework?
A: The choice of a testing framework depends on several factors, such as the specific needs of your project, familiarity with the tool, community support, and integration capabilities with other tools and systems.
Happy (automated) testing!