🤖 Summarize this article with AI:
💬 ChatGPT 🔍 Perplexity 💥 Claude 🐦 Grok 🔮 Google AI Mode
Software development has changed faster than testing processes have kept up.
A decade ago, manual testing was the default — slow but manageable. Teams could afford to click through test cases, file bugs, and repeat. However, with today’s CI/CD pipelines, weekly releases, and agile sprints, that manual approach can no longer sustain quality.
🎯 TL;DR - What is Automated Testing?
- Manual-only testing can’t keep up with modern CI/CD. Frequent releases and agile cycles demand automation to scale repetitive checks and maintain quality.
- How it works: define scenarios → execute automatically (often in CI) → validate outcomes → generate reports for fast, objective feedback.
- Use both manual and automated testing. Manual excels at exploratory/UX judgment; automation shines for regression, smoke, E2E, and data-driven tests—run consistently across environments.
- What to automate first & where: prioritize stable, high-value flows (auth, checkout, core forms/APIs). Mix test types (unit, integration/API, UI, regression/smoke, performance/security/compatibility) based on risk and stability.
- Build a sustainable automation practice. Focus on maintainability, reliability, scalability, and reusability; choose tools that fit team skills (e.g., Selenium/Cypress/Playwright or codeless options like BugBug) to reduce upkeep and speed up delivery—paying off in faster cycles, higher confidence, and lower costs.
Also check:
- 🎯 TL;DR - What is Automated Testing?
- What Is Test Automation? (Definition + Core Concept)
- How Automated Testing Works (With Example)
- Automation Testing vs Manual Testing
- Types of Automated Testing
- What Should You Automate First?
- The Pillars and Approaches of Test Automation
- Common Tools for Automation Testing
- Is Automation Testing Easy (and Worth It?)
- Key Takeaways & Next Steps
- FAQ - Automation Testing

What Is Test Automation? (Definition + Core Concept)
At its core, automation testing — often called test automation or automated testing — is the practice of using specialized tools to execute pre-scripted tests on software applications. Instead of a human manually clicking buttons or typing inputs, the testing tool performs those same actions automatically, compares actual results to expected ones, and reports any discrepancies.
Think of it as delegating repetitive verification work to a dependable assistant that never gets tired, distracted, or inconsistent.
Automation testing exists to solve one fundamental problem: manual testing doesn’t scale.
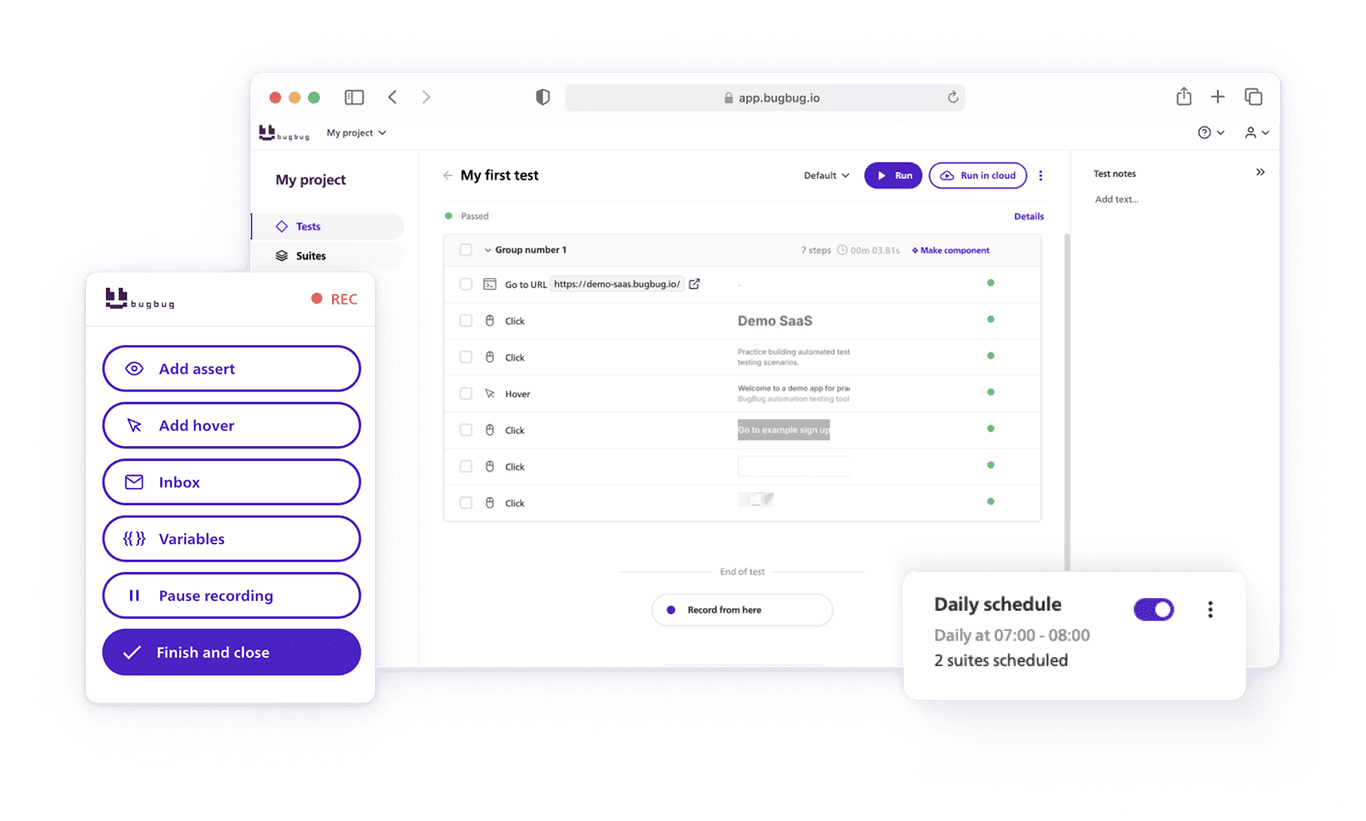
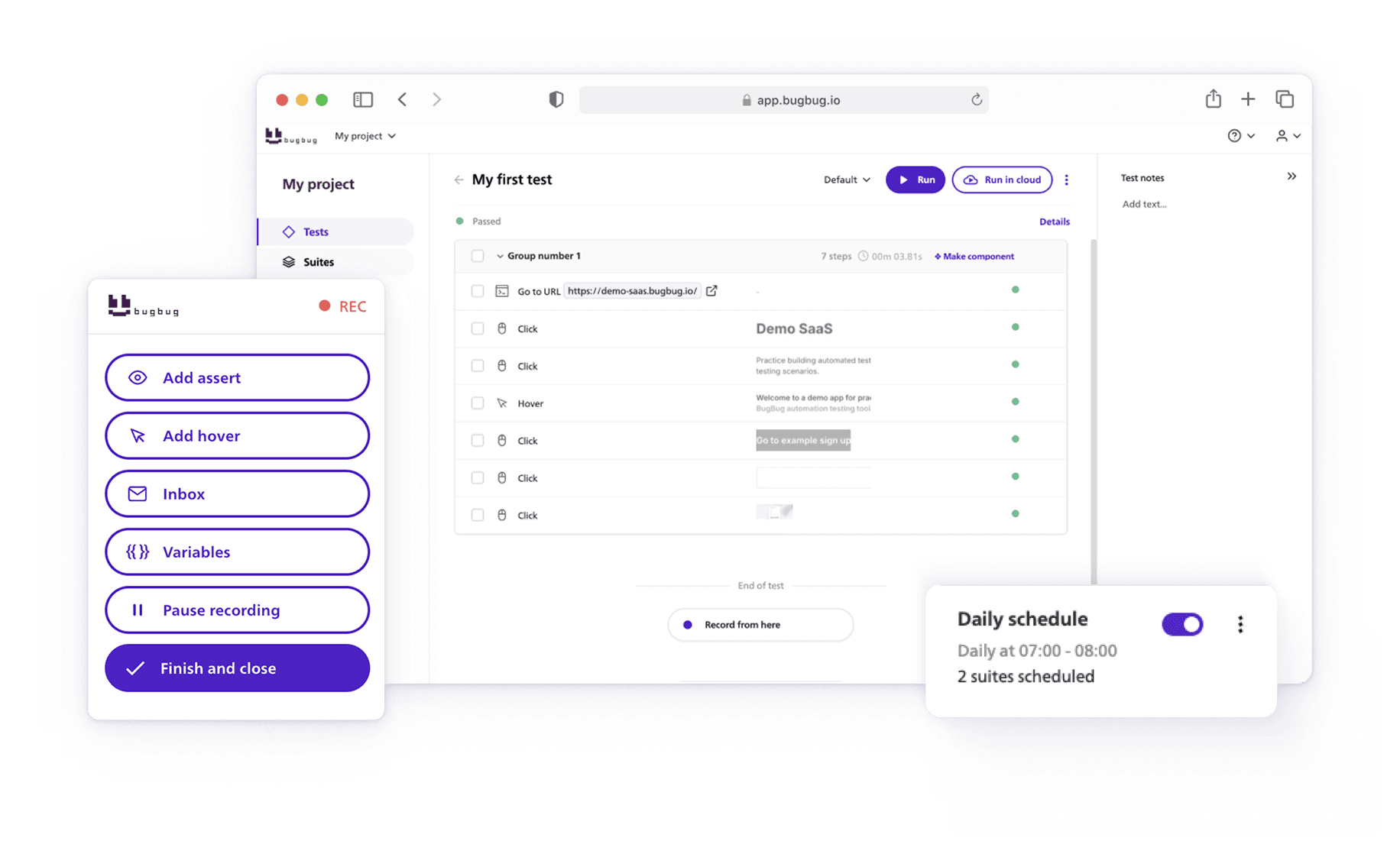
But automation testing isn’t just for massive enterprise teams anymore. Modern, no-code tools like BugBug make this process accessible to everyone — from startup founders validating their MVP to QA engineers building robust regression suites. With BugBug, you can record user flows visually, run them in the cloud, and integrate with your CI/CD pipeline — all without touching a single line of code. These modern tools make it easier than ever to automate software testing for teams of any size.
How Automated Testing Works (With Example)
Every automation framework — whether it’s Selenium, Cypress, or BugBug — follows the same basic principle: define the behavior you want to test, automate its execution, and verify the outcome.
Let’s break that down into clear stages. The test automation process involves defining, executing, and validating tests.
1. Define the Test Scenario
You start by describing what you want to test — for instance,
When a user enters valid credentials and clicks Login, they should be redirected to the dashboard.” For automated testing of this workflow, use test automation tool like BugBug.io.
That scenario becomes your test case.
Automate your tests for free
Test easier than ever with BugBug test recorder. Faster than coding. Free forever.
Get started
2. Execute the Test Automatically
Once defined, the test can be executed at any time — manually or on a schedule.
The tool simulates real user actions in a browser: clicking, typing, scrolling, submitting forms. It does exactly what a human tester would do, but far faster and more consistently.
In a CI/CD pipeline, tests might run automatically:
- After each code commit
- Before deployment
- On a nightly or weekly schedule
This continuous execution ensures bugs are caught early, long before they reach production.
3. Validate the Results
Automation testing doesn’t just perform actions — it checks outcomes.
The tool compares what actually happened against the expected behavior defined in your test case.
For example:
- Did the login form redirect to the correct page?
- Did the success message appear?
- Were the correct elements visible or enabled?
If something doesn’t match expectations, the test fails — signaling a potential regression.
4. Generate Reports and Insights
The final step is feedback.
Automation tools provide detailed reports showing which tests passed, which failed, and why.
This gives QA and development teams fast, objective feedback that drives better collaboration and faster fixes.
Automation Testing vs Manual Testing
If you’ve worked in QA, you know there’s a long-standing debate: _“Should we automate everything, or keep some tests manual?”_The honest answer? You need both. Each approach serves a distinct purpose — and understanding when to use which can save your team weeks of wasted effort. A manual tester is often required to perform repetitive tasks, which can lead to human errors and increased manual effort.
Manual Testing: When Human Insight Matters
Manual testing is still the foundation of quality assurance. It’s human-driven, intuitive, and flexible — perfect for:
- Exploratory testing – discovering unexpected behavior that scripts can’t anticipate.
- Usability and UX testing – judging visual appeal, clarity, or emotional response.
- Ad hoc testing – checking quick fixes or edge cases before full automation.
Manual testing shines in contexts where judgment and creativity matter.
A skilled QA engineer can catch subtle UI misalignments, confusing interactions, or missing microcopy — things an automated script would never notice.
However, manual testing doesn’t scale.
Running the same login or checkout flow across five browsers, three environments, and multiple releases is not only tedious — it’s error-prone and expensive. That’s where automation steps in.
Automation Testing: When Speed and Consistency Win
Automation testing replaces manual repetition with precision and speed.
It’s ideal for:
- Regression testing after every new deployment.
- Smoke testing to confirm builds are stable.
- End-to-end testing to verify complete user journeys.
- Data-driven testing where multiple inputs must be validated.
Once you’ve automated a test, it can run hundreds of times without additional effort.
You gain repeatability, coverage, and speed — especially critical in agile environments where code changes daily.
Automation also brings consistency: the same test runs exactly the same way, every time, eliminating the variability of human testers.
That consistency builds confidence in each release, freeing QA teams to focus on higher-value analysis instead of repetitive execution.
Try automation testing with BugBug
Test easier than ever with BugBug test recorder. Faster than coding. Free forever.
Get started
Finding the Right Balance: Manual + Automated Testing
The smartest teams combine both.
- Use manual testing early in development — to explore, prototype, and validate usability.
- Transition stable, high-impact flows to automation once they’re mature.
- Keep automation suites lean by focusing on critical paths (login, checkout, API endpoints).
This hybrid model ensures you cover what humans do best — intuition and empathy — and what machines do best — speed and reliability.
Types of Automated Testing
Automation testing isn’t one-size-fits-all. Different layers of your application call for different types of tests. Smart QA teams automate what’s stable, repetitive, and business-critical, while keeping exploratory or fast-changing areas manual.
Here are the key types of automation testing — and where tools like BugBug can help. Key types of software tests that can be automated include unit test, integration tests, functional testing, performance tests, regression tests, and smoke test. Exploratory and functional testing are also important; exploratory testing is often performed manually, while functional tests are prime candidates for automation.
Unit Testing
Purpose: Test individual functions or methods in isolation with a unit test.
Why it matters: Catches bugs early before integration.
Tools: Jest, NUnit, JUnit (a popular unit testing framework for Java that supports automated unit test creation and execution).
Tip: Keep unit tests small and fast; run them on every commit.
Integration Testing & API Testing
Purpose: Ensure modules, services, and APIs communicate correctly. Integration tests verify how different modules or components work together, ensuring system reliability.
Why it matters: Even working units can fail when connected.
Tools: Postman, REST Assured, pytest.
BugBug relevance: Can simulate integration through UI flows that trigger backend calls.
UI Testing
Purpose: Verify that the user interface behaves correctly across browsers.
Why it matters: Confirms users can interact with your app without friction.
Example: Logging in, adding items to cart, or submitting a form.
BugBug: Codeless, visual UI testing for web apps — record once, run anywhere.
Regression & Smoke Testing
Purpose: Catch bugs introduced by new code or broken builds by running smoke tests and regression tests.
Why it matters: Smoke tests provide a quick, initial check to ensure basic functionality is working after a new build, while regression tests verify that new changes do not break existing features. Both types of tests protect existing functionality and save QA time.
Example: Running a smoke test on key flows like login or checkout after deployment to quickly assess stability, followed by automated regression tests to ensure all existing features still work as expected.
👉 Check also: How to scale test automation without code?
Functional & End-to-End Testing
Purpose: Validate complete business workflows and user journeys. Functional testing validates application features, workflows, and business logic, while functional tests are essential for ensuring correct system behavior across different scenarios.
Why it matters: E2e testing ensures the product performs as intended from start to finish.
Example: Signup → verify email → purchase → confirmation.
Performance, Security & Compatibility Testing
Purpose: Measure stability, protect against vulnerabilities, and ensure cross-browser consistency. Performance tests and performance testing evaluate how well an application functions under expected workloads, focusing on responsiveness and stability.
Why it matters: Real users access your app on different devices, browsers, and speeds.
Tools: JMeter, OWASP ZAP, K6.
What Should You Automate First?
If you’re starting fresh, don’t try to automate everything. Focus on high-value, low-volatility areas that deliver immediate ROI:
- User authentication (login, signup)
- Core purchase or checkout flows
- Critical data inputs (forms, search, filters)
- Navigation paths and dashboards
- API endpoints supporting core features
Prioritizing repeatable tests and ensuring the same tests are executed across different environments maximizes the benefits of automation by increasing reliability and consistency.
The Pillars and Approaches of Test Automation
Automation testing isn’t just about writing scripts or recording steps — it’s about building a sustainable testing ecosystem that scales as your product evolves.
Teams that rush into automation often hit walls: brittle tests, frequent failures, or endless maintenance. The difference between a fragile test suite and a reliable one lies in the four key pillars of test automation. A well-defined test automation strategy and adherence to best practices are essential for ensuring long-term success and reliability in your automation efforts.
Maintainability — The Ability to Evolve with Your App
Your test suite should grow with your product, not against it.
Maintainability means tests are easy to read, edit, and update when your app’s UI or logic changes.
Poorly structured tests often break with every CSS tweak or layout shift — leading to frustration and ignored automation.
To ensure maintainability:
- Use clear, descriptive test names.
- Organize tests by user journey or feature.
- Reuse common steps (e.g., login, search) instead of duplicating them.
- Keep test data external and version-controlled.
Read also
Reliability — Trust That Tests Reflect Reality
Automation is only useful if you can trust the results.
Unreliable tests — those that fail randomly or produce false positives — erode confidence and slow teams down.
To improve reliability:
- Avoid relying on unstable UI selectors.
- Wait for elements to load dynamically (avoid hard-coded delays).
- Run tests across consistent environments and data states.
Scalability — Handling Growth Without Chaos
As your app grows, so will your test suite.
Scalability means you can run more tests, across more environments, without extra maintenance overhead.
In traditional script-based frameworks, scaling often means adding servers, configuring parallel runners, or maintaining complex pipelines.
In codeless tools like BugBug, scaling is visual and lightweight:
- Run tests in the cloud or headless mode.
- Trigger tests from CI/CD pipelines automatically.
- Schedule daily, weekly, or post-deployment test suites.
💡 Tip: Focus on quality over quantity. 200 well-designed, maintainable tests beat 1,000 flaky ones.
Reusability — Automate Once, Use Everywhere
Good automation frameworks are modular. You shouldn’t have to rewrite the same steps for each scenario.
Reusability means:
- Breaking tests into small, logical chunks.
- Centralizing repeated flows (like authentication).
- Parameterizing inputs to cover multiple data cases.
The Two Main Approaches to Automation Testing
Once you understand the pillars, the next question is how to implement them.
When choosing between automation approaches, consider that software coding ability and the choice of programming language play a significant role in selecting suitable automation tools and frameworks. Broadly speaking, teams choose between script-based and codeless (no-code) automation — or a hybrid of both.
Script-Based Automation
This approach uses code to define tests, often in languages like JavaScript, Python, or Java. Engineers write automated tests and write tests as source code to define and execute automated checks, enabling precise control over test logic and execution. It offers full flexibility and customization but requires engineering expertise and maintenance resources.
Pros:
- Highly customizable
- Deep integration with CI/CD pipelines
- Suitable for complex, API-heavy projects
Cons:
- Steep learning curve
- High setup and maintenance cost
- Difficult for non-developers to contribute
Codeless Automation
Codeless automation tools like BugBug allow you to record, edit, and maintain tests visually, removing the barrier of programming. Features such as test data creation further simplify the process of building and maintaining automated tests, making it easier to automate tasks like product installation, GUI interaction, and defect logging. They’re designed for speed, accessibility, and collaboration — enabling QA engineers, product managers, and even designers to participate in test creation.
Pros:
- Fast to start — no setup, no frameworks
- Easy for cross-functional teams
- Ideal for UI and end-to-end testing
- Simplified maintenance
Cons:
- Less flexible for backend or API-heavy testing
- Limited for highly customized workflows
Common Tools for Automation Testing
The automation testing landscape is broad — and honestly, a bit overwhelming. There are a wide variety of automation testing tools, test automation tools, and popular automation testing tools available in the market today. Choosing the right automation tool is crucial for meeting your team’s skills, project scope, and release velocity.
From open-source frameworks to cloud platforms and no-code tools, there’s no single “best” solution. The right choice depends on your team’s skills, project scope, and release velocity. Many popular test automation tools are widely used in the industry for their ability to enhance software quality and improve testing efficiency.
Whether you’re testing a SaaS dashboard, an e-commerce checkout, or a microservices API, your goal is the same: stable, maintainable automation that fits your workflow.
BugBug — The Lightweight, Codeless Alternative
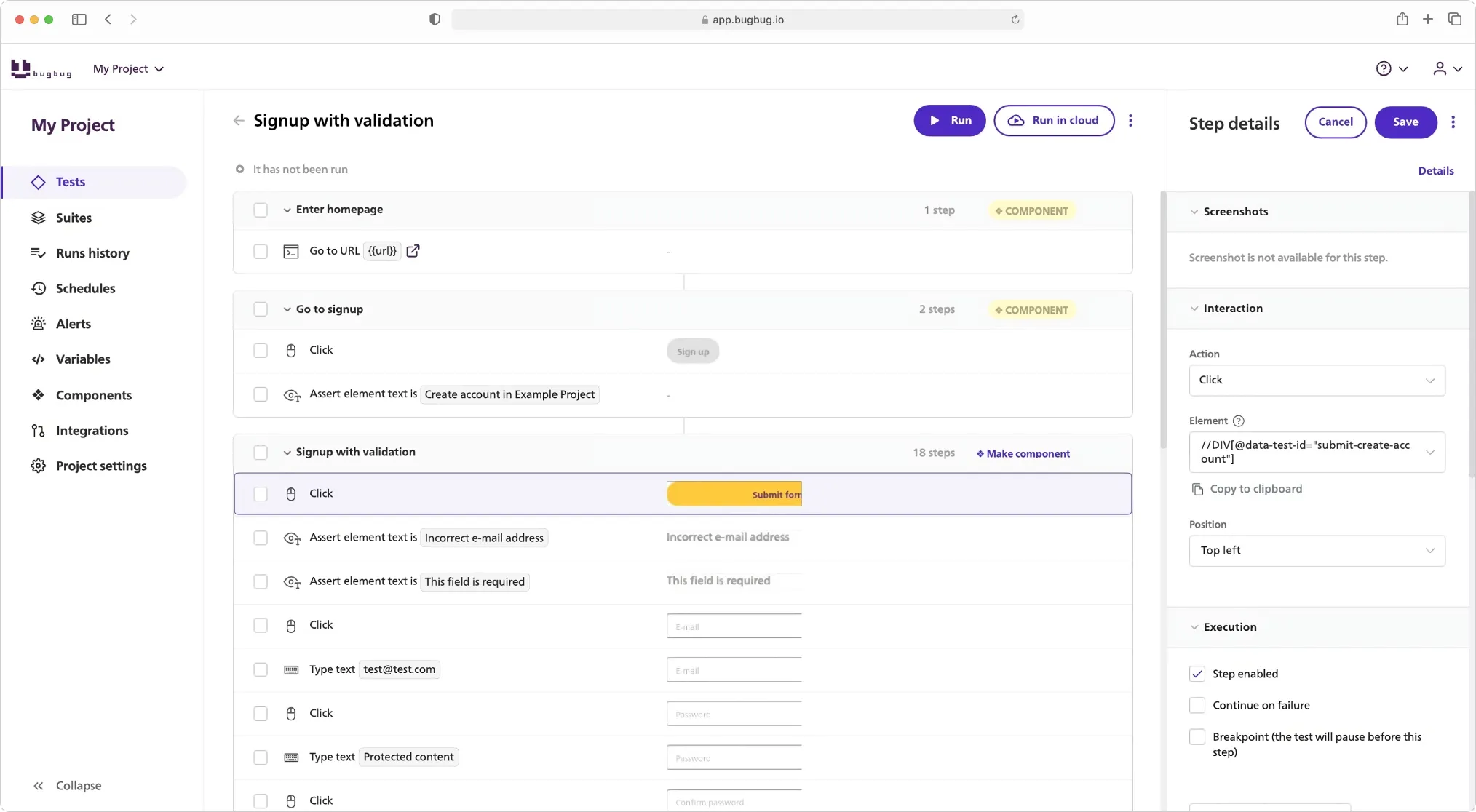
BugBug is a codeless automation testing tool focused on speed, simplicity, and accessibility.
It allows you to record, edit, and run browser-based tests visually — directly from your browser, no installation or scripts required.
Strengths:
- No coding or setup needed — ideal for small teams and startups
- Built specifically for web applications
- Record tests once, reuse them across multiple environments
- Reusable components for maintainability
- Integrated scheduling, API triggers, and CI/CD compatibility
- Minimal maintenance compared to script-based tools
Limitations:
- Focused on UI and end-to-end testing (not backend-heavy apps)
- Currently optimized for Chromium browsers
Best for:
QA teams, developers, and startup founders who want fast, reliable test automation without the setup burden. Perfect for teams transitioning from manual to automated testing.
Selenium — The Veteran Workhorse

Selenium is the oldest and most well-known framework for browser automation. It supports multiple programming languages (Java, Python, C#, JavaScript) and integrates with nearly every CI/CD tool.
Strengths:
- Extremely flexible and extensible
- Works across all major browsers
- Large open-source community
- Ideal for developers who prefer full control
Limitations:
- Requires coding knowledge
- Setup can be complex (drivers, environments, dependencies)
- Maintenance overhead is high for large suites
- Debugging flaky tests can be time-consuming
Best for: Teams with strong development resources and long-term test infrastructure needs.
Cypress — The Modern Developer’s Favorite

Cypress is a fast, developer-centric testing framework built for JavaScript apps. It runs directly in the browser, giving testers a visual view of how each test executes.
Strengths:
- Simple local setup
- Fast execution and interactive debugging
- Excellent for single-page applications (SPAs)
- Built-in dashboard for analytics and CI integration
Limitations:
- Limited cross-browser support (mostly Chromium)
- API and backend testing capabilities are minimal
- Requires JavaScript skills for scripting
Best for: Frontend-heavy teams comfortable with JavaScript and looking for speed in test feedback.
Playwright — The Powerful All-Rounder

Playwright, developed by Microsoft, is a next-generation browser automation framework similar to Cypress — but with more flexibility. It supports multiple languages and browsers out of the box. Tools like Playwright often require accurate XPath selectors for automating web interactions.
Strengths:
- Works with Chromium, Firefox, and WebKit
- Great for cross-browser testing
- Advanced features (network mocking, tracing, parallelization)
- Supports UI, API, and visual regression testing
Limitations:
- Requires scripting skills and setup
- Can be overkill for small QA teams
- More complex to maintain for non-developers
Best for: Engineering-driven QA teams testing at scale across browsers and devices.
Choosing the Right Tool for Your Team
Here’s a quick comparison to help you visualize the trade-offs:
| Tool | Skill Required | Setup Effort | Best Use Case | Maintenance Effort | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Selenium | High | Complex | Cross-browser, enterprise QA | High | Dev-heavy QA teams |
| Cypress | Medium | Moderate | SPAs, fast dev feedback | Moderate | JS-focused frontend teams |
| Playwright | Medium | Moderate | Cross-browser, API + UI | Moderate | Engineering-led QA |
| BugBug | Low (No-Code) | Minimal | UI & E2E for web apps | Low | Small QA teams, startups, hybrid workflows |
When choosing the right tool, consider how well it integrates into your software development process. Effective integration of automation testing tools not only streamlines workflows but also plays a crucial role in improving software quality by enabling early bug detection and consistent testing throughout development.
Is Automation Testing Easy (and Worth It?)
Let’s be honest — automation testing isn’t easy when you’re starting out. It demands a shift in mindset, process, and tooling. You move from exploring applications manually to thinking in repeatable steps, data flows, and validation logic.
However, automation testing significantly reduces manual effort by eliminating repetitive tasks and repetitive tests, allowing QA teams to focus on higher-value activities.
But here’s the thing: once you pass that initial learning curve, automation testing doesn’t just make QA easier — it changes the role of QA entirely.
The Reality: Automation Takes Effort Upfront
The first challenge most teams face is setup. Installing frameworks, configuring drivers, managing environments, and writing stable scripts can consume weeks before the first test even runs. However, this initial investment pays off when automation tests and automation test suites are running efficiently, enabling faster, more reliable, and scalable testing.
That’s why many QA teams hesitate to start — especially in small organizations where testers wear multiple hats.
Traditional frameworks like Selenium or Playwright require:
- Coding knowledge
- Continuous maintenance
- A reliable CI/CD setup
- And often, developer support
The result? Valuable time is spent managing the framework instead of testing.
This is exactly where modern no-code tools like BugBug are changing the game. You can record user flows directly in your browser, define validation points visually, and schedule tests instantly — no installation, no scripting, no DevOps dependency.
For many teams, that’s the difference between “we should automate” and “we automated it today.”
The Payoff: Speed, Confidence, and Cost Savings
Once automation is in place, the benefits are exponential. Instead of spending hours manually checking the same flow, your tests run automatically — after every commit, every night, or every deployment.
Here’s what automation brings to your QA process:
- Speed: Test cycles shrink from days to minutes.
- Reliability: Machines don’t forget steps or miss bugs due to fatigue.
- Coverage: You can run hundreds of scenarios across browsers, devices, and environments.
- Consistency: Each test executes exactly the same way, every time.
- Scalability: Add new tests without adding new testers.
- Software Quality: Automation testing improves software quality by reducing errors, enabling early bug detection, and ensuring better test coverage throughout the development cycle.
A well-built automation suite can save hundreds of QA hours per month. But beyond efficiency, automation transforms how QA collaborates with development — shifting testing earlier into the delivery pipeline (the “shift-left” principle). Bugs are caught early, fixes are cheaper, and releases become routine rather than stressful.
The Verdict: Worth Every Step
Automation testing demands patience in the beginning. You’ll debug flaky selectors, organize test data, and rethink your test design approach. But the test automation ROI — in time, confidence, and professional growth — is undeniable.
Integrating automation testing throughout the software development lifecycle ensures greater efficiency, accuracy, and test coverage at every stage of development.
Key Takeaways & Next Steps
Automation testing is no longer just a “nice-to-have.” It’s the backbone of modern software development — the key to delivering faster, safer, and more reliable releases.
But automation isn’t about chasing buzzwords. It’s about building a dependable testing rhythm that fits your team’s workflow and helps you ship with confidence. Effective automation also relies on proper test data creation and following a structured test automation process to ensure comprehensive and reliable results.
Ready to Start Automating?
💡 If you’ve ever felt that test automation was too complex or too technical — BugBug proves it doesn’t have to be.
In just a few minutes, you can:
- Record your first test visually
- Run it in the cloud
- Schedule it to repeat after every deployment
No code. No setup. No maintenance headaches.
Just smooth, reliable automation that fits your team’s pace.
Happy (automated) testing!