🤖 Summarize this article with AI:
💬 ChatGPT 🔍 Perplexity 💥 Claude 🐦 Grok 🔮 Google AI Mode
Software testing is the safety net of modern software development. It ensures that your product not only functions correctly but also delivers a consistent and reliable user experience. Software testing is the process of evaluating, verifying, and ensuring the functionality, quality, and reliability of a software application throughout its software development life cycle. Without a proper testing process, even a single unnoticed bug can crash a critical feature, damage user trust, and slow down your release cycle.
In the fast-paced world of continuous delivery, testing has evolved far beyond manual QA checklists. It’s now a combination of strategic thinking, automation, and collaboration between developers, testers, and product teams. Quality assurance is a key goal of software testing, ensuring reliability and high standards throughout the software development life cycle. This guide will take you through the fundamentals of software testing, explain its different types, and show how modern tools like BugBug simplify the process so you can focus on building, not babysitting tests.
Understanding the benefits of software testing—such as improved product quality, reduced costs, and increased user satisfaction—demonstrates why it is essential at every stage of the software development life cycle.
- Why Software Testing Still Matters in 2026
- Software Testing - What Is It?
- Why Software Testing Is Crucial for Every Product
- The Main Types of Software Testing
- The Software Testing Process: From Planning to Reporting
- Manual vs Automated Testing: Finding the Right Balance
- The Rise of Test Automation
- How to Choose the Right Type of Testing for Your Project
- Conclusion: Testing Is Software’s Lifeline
- FAQ - Software Testing Basics
Check also:
Why Software Testing Still Matters in 2026
You might think automation and CI/CD pipelines already handle everything — but testing remains the heart of software quality. Continuous testing throughout the development process is essential for delivering high quality software, as it ensures that issues are identified and addressed at every stage.
Software today is more interconnected than ever. Microservices, APIs, browser extensions, and device variations mean there are countless ways things can go wrong. Without testing, small changes can trigger regressions that ripple across the product.
Software testing helps you:
- Detect issues early before users find them.
- Maintain confidence in rapid releases.
- Keep development agile while reducing manual overhead.
- Ensure quality at every stage of the development process through continuous testing.
For startups and lean development teams, the challenge is maintaining this quality without adding unnecessary complexity. That’s why lightweight, no-code solutions like BugBug are gaining traction — offering a visual, browser-based approach to automation that doesn’t require dedicated QA infrastructure or scripting skills.
Software Testing - What Is It?
At its simplest, software testing means evaluating an application to ensure it behaves as expected. But in practice, it’s a discipline of risk reduction — confirming that your app delivers value without introducing defects, performance issues, or security risks.
Testing answers two essential questions:
- Verification: Are we building the product right? (Does it meet the requirements?)
- Validation: Are we building the right product? (Does it meet user needs?)
There are two main approaches:
- Manual testing: Manual testing involves testers executing test cases without automation. Human testers interact with the product, explore flows, and record observations.
- Automated testing: Tools execute pre-defined steps repeatedly, comparing actual vs expected results. Automated testing uses test scripts to automate test execution, increasing speed, accuracy, and reusability during software testing and regression testing.
Automation shines in repeatability — regression testing, smoke testing, or CI/CD pipelines — where consistency matters most. For example, instead of manually checking whether your checkout still works after every deployment, BugBug can automatically run this scenario across browsers, ensuring that updates never break key flows.
Pro tip: Combine manual testing for discovery with automated testing for reliability. You’ll cover both creative and repetitive testing needs. Both manual and automated approaches require careful test case design and execution.
👉 Check our automation testing tutorial for beginners
Why Software Testing Is Crucial for Every Product
Testing isn’t an optional step; it’s a continuous process that safeguards every stage of development. Software testers analyze test results and document their findings in a test report to ensure product quality. Here’s what’s at stake:
Enhance Product Quality
Quality isn’t about adding more tests — it’s about ensuring your product meets user expectations under real conditions.
By running targeted, well-designed tests, teams can spot inconsistencies early and fix them before they spread across releases. Automated testing tools help maintain this consistency even when development velocity increases.
Improve Security
Every new feature introduces potential vulnerabilities. Testing helps teams uncover hidden risks such as unsafe data storage, weak authentication, or misconfigured APIs.
Security testing, combined with unit and integration checks, forms a multi-layered defense that protects users and the business alike.
Ensure Compatibility Across Environments
Your app might work perfectly on Chrome but fail on Safari or a mobile browser.
Cross-browser and cross-platform testing ensure a unified experience across environments. BugBug helps by running real browser sessions, so what’s tested truly reflects what users experience in production.
The Main Types of Software Testing
Software testing isn’t a single activity — it’s a framework of approaches tailored to different goals. There are various software testing types, each designed to address specific aspects of software quality. Different testing techniques are applied to these types to achieve comprehensive test coverage and ensure reliability.
Here’s a breakdown every QA and developer should know:
Before diving into the details, it's important to understand the test pyramid model. This model structures software testing types into a hierarchy—unit tests at the base, followed by integration tests, and UI tests at the top—promoting efficient, scalable, and automated testing processes that maximize test coverage.
Functional Testing
Functional testing verifies that the software functions as intended by checking that each feature meets specified requirements and behaves as expected from an end-user perspective. It validates the logic, flow, and outcomes of each feature to ensure alignment with business and technical specifications.
Common subtypes include:
- Unit Testing: Developers test individual components or functions in isolation to ensure each part works correctly before integration.
- Integration Testing: Ensures that different modules communicate correctly.
- System Testing: Evaluates the entire application end-to-end.
- End-to-End (E2E) Testing: Simulates real user behavior from start to finish — e.g., signing up, logging in, and making a purchase.
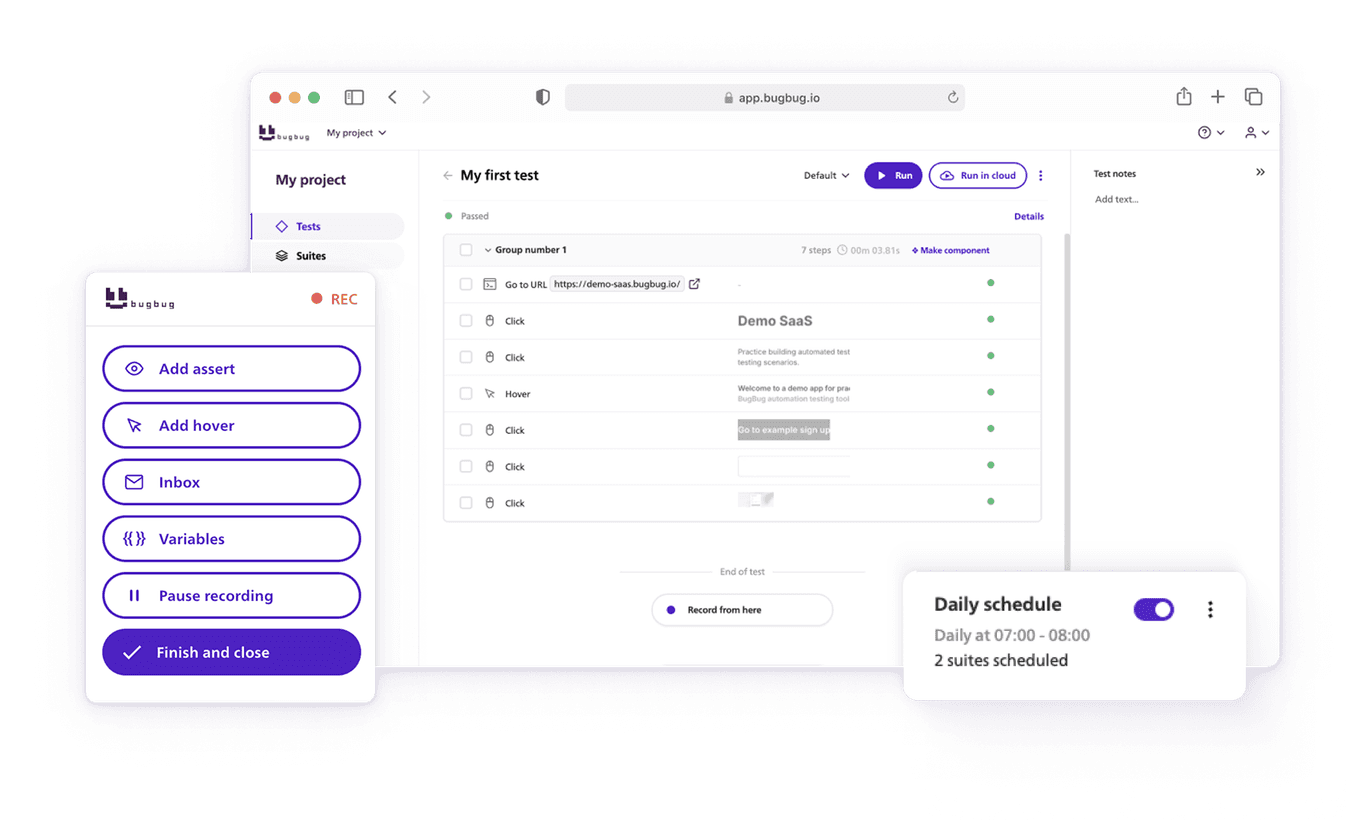
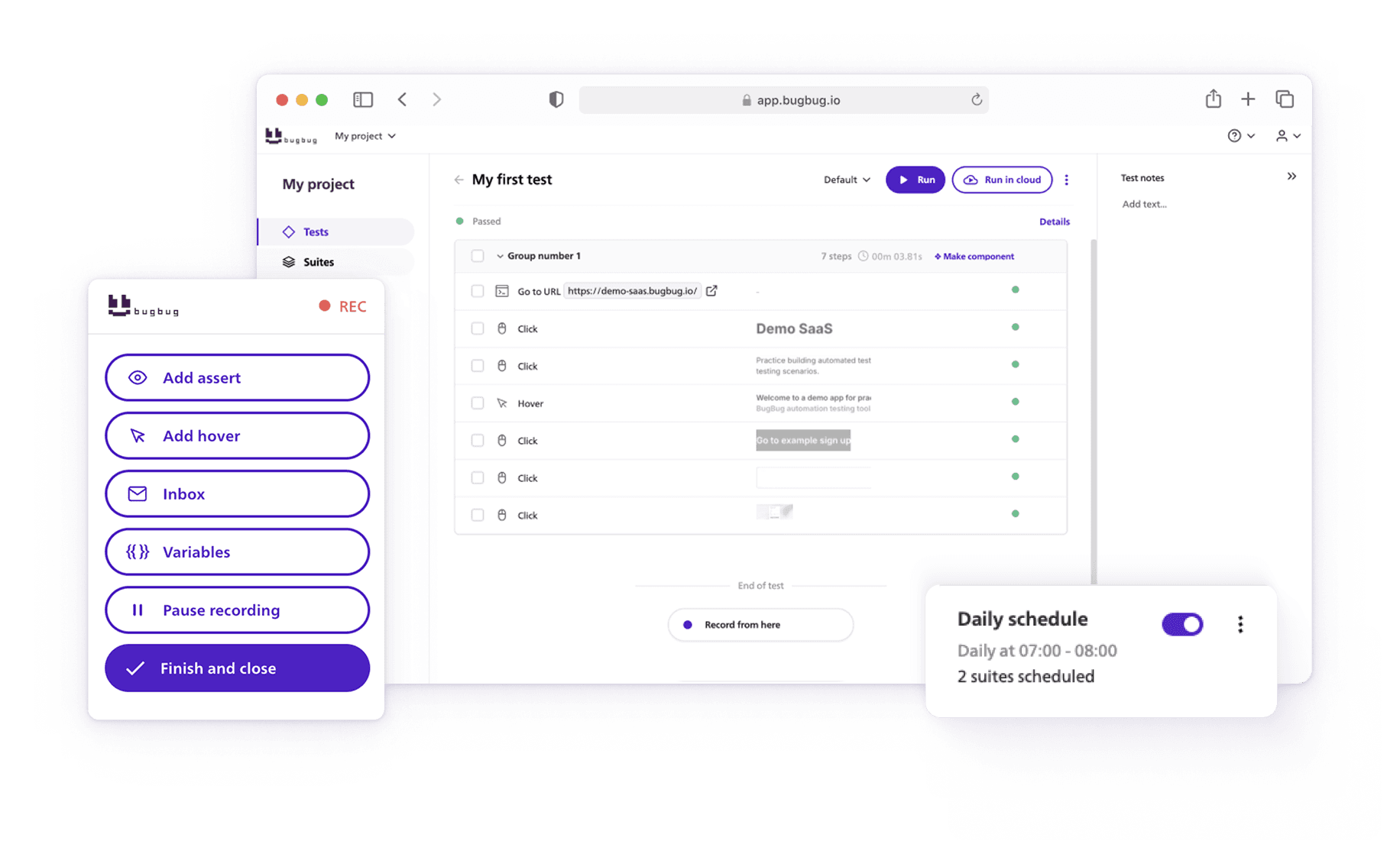
BugBug is built specifically for E2E testing, letting teams record and run full user flows with a simple, visual interface. No scripts, no setup — just reliable automation.
Non-Functional Testing
While functional tests focus on “what” the system does, non-functional testing checks “how well” it does it. Key areas include:
- Performance & Load Testing: Measures responsiveness and stability under heavy usage.
- Stress Testing: Assesses system performance under extreme conditions to ensure stability and reliability.
- Usability Testing: Evaluates how easy and intuitive the interface is.
- Security Testing: Identifies vulnerabilities.
- Compatibility Testing: Confirms that the app works across browsers and operating systems.
These tests ensure the product meets performance standards beyond just functionality.
Testing Approaches: Black-box, White-box, Grey-box
- Black-box testing: The tester doesn’t know the internal code structure — focuses purely on inputs and outputs. Ideal for UI and acceptance testing.
- White-box testing: Involves code-level knowledge. Developers verify internal logic, algorithms, and data paths.
- Grey-box testing: A mix — where testers understand system internals enough to create smarter, more targeted test cases.
For front-end testing, BugBug uses the black-box approach, enabling realistic end-to-end scenarios that mirror user behavior.
Exploratory & Gorilla Testing
- Exploratory Testing: QAs use intuition and experience to explore the app in unpredictable ways, uncovering bugs that scripted tests miss.
- Gorilla Testing: This is a type of software testing focused on manual, repeated testing of selected modules with random inputs. It repetitively tests a single feature until it breaks, uncovering hidden issues.
Both are invaluable in early-stage testing when creativity and curiosity matter more than coverage.
The Software Testing Process: From Planning to Reporting
A successful software testing life cycle consists of several testing phases, including test planning, test execution, and reporting. Whether manual or automated, these steps ensure discipline and traceability.
Planning
Define objectives and scope. Which features need testing? What are the priorities?
For example, e-commerce teams might prioritize checkout and payment flows, while SaaS teams focus on login and dashboard performance.
Test Preparation
Prepare your test data, environment, and test cases.
Instead of coding each scenario from scratch, BugBug allows teams to record a test visually — interacting with the application just like a user would. This drastically reduces setup time.
Execution
Run your tests in a controlled environment.
Automation enables parallel execution, saving hours compared to manual runs. BugBug can execute multiple E2E tests after every deployment, automatically verifying that key workflows remain intact.
Reporting & Analysis
Testing without analysis is wasted effort.
Use reports to identify recurring failures, track progress, and make informed release decisions. BugBug’s dashboard helps visualize results, making it easier for teams to collaborate and share testing insights.
Manual vs Automated Testing: Finding the Right Balance
Both manual and automated testing have their strengths:
| Manual Testing | Automated Testing |
|---|---|
| Flexible and intuitive | Fast and repeatable |
| Great for usability and exploratory testing | Ideal for regression and CI/CD |
| Relies on human judgment | Reduces human error |
| Time-consuming | Requires upfront setup |
| Manual software testing is essential for exploratory, usability, and ad-hoc scenarios that require human judgment. | Automated software testing and automation testing use automated tools to efficiently handle repetitive tasks and repetitive testing tasks, improving accuracy and scalability. |
The goal isn’t to replace manual testers — it’s to empower them. Automation handles repetition so testers can focus on creative, high-value scenarios.
BugBug fits perfectly here: it bridges the gap between manual intuition and automated precision, letting non-technical team members create powerful tests visually.
The Rise of Test Automation
Test automation has moved from a nice-to-have to an absolute necessity. Agile development, DevOps, and frequent deployments demand rapid feedback loops that only automation can deliver. Over the years, software testing tools have evolved significantly, making it crucial to choose the right testing tool for automation to ensure efficiency and reliability.
The Test Automation Pyramid illustrates the optimal balance:
- Unit Tests (Base): Validate individual code units.
- Integration Tests: Check communication between modules.
- End-to-End Tests (Top): Verify real-world scenarios across the entire app.
E2E tests are the most critical — but also historically the hardest to maintain. BugBug simplifies this layer by offering:
- No-code test creation
- Real browser execution
- Automatic replays for regression detection
- Cloud-based scheduling for hands-off testing
- Easy creation of test scripts and the ability to execute test cases without coding
This makes it feasible for small teams to maintain confidence without overengineering their QA setup. Modern tools now enable teams to run tests efficiently and reliably.
How to Choose the Right Type of Testing for Your Project
Choosing the right testing strategy depends on several variables:
- Product complexity: Larger systems need layered testing.
- Team structure: Smaller teams may prioritize automation tools that require minimal maintenance.
- Release cadence: Frequent updates demand CI-integrated automated tests.
- Risk profile: Mission-critical systems (e.g., fintech) need deeper testing coverage.
💡 Check our detailed guide on the different types of testing
The development team should align testing activities with each development phase of the software development lifecycle to ensure that quality is built in from the start.
Example approach:
- Use unit tests to secure core logic.
- Add integration tests to validate component interaction.
- Automate end-to-end flows (with BugBug) to ensure users can complete essential tasks seamlessly.
- Supplement with exploratory testing to catch unexpected issues.
Testing should be integrated throughout the development cycle to ensure quality at every stage.
This layered approach delivers coverage, speed, and confidence — without overwhelming the team.
Conclusion: Testing Is Software’s Lifeline
Every reliable product you use today owes its stability to disciplined testing. It’s what allows developers to innovate confidently and ship features without fear. In conclusion, software testing with the right types and tools guarantees quality, meets customer expectations, and enhances application performance.
Testing isn’t a blocker; it’s a multiplier of velocity.
The key isn’t to test more — it’s to test smarter. Modern automation tools have made that possible even for small teams with limited QA resources.
BugBug takes this philosophy seriously. It lets anyone — from testers to PMs — create, run, and maintain end-to-end browser tests without writing code. That means faster iterations, fewer regressions, and more confidence in every release.
Ready to automate your first test? Start for free at bugbug.io — and see how easy reliable testing can be.
Happy (automated) testing!