🤖 Summarize this article with AI:
💬 ChatGPT 🔍 Perplexity 💥 Claude 🐦 Grok 🔮 Google AI Mode
- Free Test Case Template (Downloadable)
- Core Categories of Search Functionality Test Cases
- Search Logic & Functional Behavior
- Input Handling & Query Parsing Test Cases
- Negative Test Cases for Search Functionality
- Search Results Evaluation Test Cases
- Performance & Reliability Test Cases for Search Functionality
- User Experience & Accessibility Test Cases
- How to Test Search Functionality More Efficiently With BugBug
- Last Thoughts
Search is one of the most deceptively complex features in any application. It looks simple—just a text box and a list of results—but the underlying system touches indexing, data quality, relevance logic, performance engineering, and UX patterns that evolve over time.
For QA teams, this creates a painful reality: if search breaks, users notice immediately.
A mistyped query not handled correctly, a slow response time, a poorly ranked result, or a missing product can directly impact conversions, retention, and trust. In many e-commerce and SaaS products, search is the primary navigation system. Ecommerce websites, in particular, face unique challenges with search functionality, such as handling large product catalogs, predictive analytics, and ensuring users can quickly find what they need.
When it fails, the whole experience feels broken. Effective search can enhance user experience by helping users find relevant information efficiently and avoid irrelevant results, which increases engagement and conversions.
This guide provides:
- 100+ search test cases, grouped into six clear, MECE categories
- real-world example test cases used in SaaS, marketplace, and e-commerce systems
- a free downloadable test case template and test plan example
- guidance on automating search flows with BugBug, including automating test cases and selecting the best tools for the job
Whether you’re building a regression suite from scratch or tightening gaps before a release, these test cases will help you ensure your search works consistently, accurately, and quickly across your site or website.
Check also:
Free Test Case Template (Downloadable)
Before diving into detailed test scenarios, here’s a ready-to-use test case template that follows QA best practices—clear steps, precise expected results, and structured data sets. This template can also serve as a test plan example for organizing and evaluating your search testing strategy.
The template includes:
- Preconditions (e.g., indexing state, login state)
- Step-by-step actions
- Input variations (keywords, filters, invalid data)
- Expected results
- Notes for automation stability
This template helps QA teams efficiently write test cases for search functionality and supports automating test cases to enhance testing accuracy and reliability.
You can use it for manual functional testing, automation, exploratory sessions, or performance preparation.
Automate your tests with BugBug
Test easier than ever with BugBug test recorder. Faster than coding. Free forever.
Get started
Core Categories of Search Functionality Test Cases
Search functionality may vary across industries, but most test scenarios fall into six universal categories. Structuring them this way prevents overlap and helps QA teams build a regression suite that is thorough without being bloated. Organizing test cases into these categories supports the overall testing lifecycle and ensures alignment with a comprehensive test plan, making it easier to manage planning, execution, and reporting.
The six categories are:
- Search Logic & Functional Behavior
- Input Handling & Query Parsing
- Negative Test Cases
- Search Results Evaluation
- Performance & Reliability
- User Experience & Accessibility
Let’s explore each in detail.
Search Logic & Functional Behavior
This category verifies the core behavior of the search engine—how it matches user queries with indexed content. It is essential to ensure the search feature works correctly, meaning the search function consistently retrieves relevant and accurate results for a wide range of search queries. Small inconsistencies in this logic can lead to incorrect results, user confusion, or lost revenue.
When matching a user's query, the product title is a key factor in the search algorithm and significantly impacts product discoverability and pageviews. Supporting search operators such as AND, OR, and NOT can further improve the accuracy of query results by allowing users to refine their searches.
Testing should include a variety of search queries to evaluate how the system interprets the user's query, including synonyms, partial matches, and misspellings. Ensuring the search feature performs consistently across the site is crucial for delivering a robust and user-friendly search experience.
Essential Test Cases
1. Exact Match Behavior
- Search for “iPhone 13” returns the correct product, ensuring accurate results for exact match queries.
- Items with identical names are ranked according to business rules.
2. Partial Keyword Matching
- “iph” or “iphon” should surface all relevant iPhone products, ensuring relevant results are displayed for partial keyword matches.
3. Multi-Keyword Queries
- “black running shoes” returns items matching all keywords, supporting multiple search terms in a single query.
4. Attribute-Based Search
- “leather bag” returns items tagged with the corresponding attribute.
5. Category-Specific Searches
- Searching while inside a category filters results correctly.
6. SKU, Model Number, or Identifier Search
- Searching “SKU-48210” returns the exact item.
7. Auto-Suggestions
- Suggestions update dynamically and reflect relevance accurately.
8. Sorting Combinations
- Sorting (price, rating) works correctly after search results load.
9. Filters + Search Interactions
- Applied filters narrow the existing result set without breaking logic.
10. Handling Out-of-Stock Items
- Out-of-stock products behave according to business rules.
11. Language and Locale Handling
- “café” returns results matching both “café” and “cafe.”
Input Handling & Query Parsing Test Cases
Even when logic is correct, search can fail at the first step: interpreting what the user typed. During the search process, it is crucial to handle unexpected inputs to ensure the search functionality remains robust and user-friendly across different scenarios. These tests verify how the system processes valid input variations and different search queries—not errors.
Key Test Cases
1. Case Insensitivity
“Laptop”, “laptop”, and “LaPTop” return the same results.
2. Whitespace Handling
Leading, trailing, and excessive internal spaces shouldn’t break results.
3. Stop Word Handling
“The office chair” ≈ “office chair”.
4. Stemming & Lemmatization
“running” matches “runner” or “run” if supported.
5. Special but Valid Characters
- “USB-C”
- “A/C unit”
- “v2.5 driver”
All should behave consistently.
6. Synonyms & Alternate Spellings
“sofa” ≈ “couch”.
7. Plural vs. Singular
“table” and “tables” return similar results.
8. Numeric Input Handling
“256GB” maps to items with that capacity.
9. Tokenization for Multi-Word Queries
“wireless noise cancelling headphones” should require all keywords.
10. Auto-Complete & Auto-Correct
Non-error auto-correct should not override queries too aggressively.
11. Emoji or Unicode Support
If supported, verify proper handling.
12. Voice Input Queries
Transcribed queries should behave like typed ones.
Negative Test Cases for Search Functionality
Negative testing ensures the system behaves safely and predictably with invalid or unusual inputs. Writing test cases that specifically target unexpected inputs helps identify and prevent irrelevant results, which can degrade user experience and lead to frustration. It is important to write test cases that cover these scenarios to ensure the search functionality remains robust and reliable.
Critical Negative Test Scenarios
1. Empty Query
System shows empty state or default results.
2. Whitespace-Only Query
Should be treated as empty input.
3. Excessively Long Strings
System truncates or safely rejects 2,000+ character inputs.
4. Unsupported Unicode
No crashes or corrupt UI components.
5. Special Characters That Should Not Be Interpreted
E.g., [], {}, *, ^, |, \
6. SQL Injection Attempts
"' OR 1=1 --"
Should never affect backend logic.
7. HTML or JavaScript Injection
UI must sanitize input to avoid XSS.
8. Irrelevant Strings
“All question marks” or random sequences → show zero-results state.
9. Invalid Filter + Query Combinations
E.g., “red shoes” + “color: blue”.
10. Typos That Should Not Be Auto-Corrected
Extreme typos shouldn’t produce misleading results.
11. Rapid or Spam Queries
Search must stay responsive and rate limiting should work.
12. Invalid Numeric Values
Negative or impossible values.
13. Filter Syntax Errors
Price min > max.
14. Backend Unavailability
Search should degrade gracefully.
15. Timeout Handling
Search should fail fast with clear messaging.
Automate your tests with BugBug
Test easier than ever with BugBug test recorder. Faster than coding. Free forever.
Get started
Search Results Evaluation Test Cases
Search may return data, but what matters is whether results are relevant, complete, and usable. It's crucial that the search results page displays accurate results that closely match the user's query, ensuring users quickly find what they are looking for. This section verifies the quality of what users see, with a focus on ensuring relevant results are prioritized.
Critical Evaluation Tests
1. Relevance Ranking
Most relevant items should appear first.
2. Completeness
No missing items that should match the query.
3. Zero-Results Handling
Clear messaging + helpful suggestions.
4. Duplicate Detection
Each product appears only once unless variations are grouped.
5. Metadata Accuracy
Correct: title, price, image, attributes, rating.
6. Click-Through Behavior
Selecting a result opens the correct page.
7. Pagination Logic
Stable results across pages; correct counts.
8. Infinite Scroll
No duplicate batches or UI jumps.
9. Sorting Consistency
Sorting must not change the result set.
10. Filtering Accuracy
Filters narrow the set correctly.
11. Keyword Highlighting
Correct terms highlighted without breaking text.
12. Personalized or Contextual Results
Behavior is predictable and consistent.
13. Fuzzy Matching
Reasonable tolerance for minor typos.
14. Out-of-Stock Handling
Correct visibility and ranking behavior.
15. High-Load Result Consistency
Rankings and pagination remain stable under stress.
Performance & Reliability Test Cases for Search Functionality
Search performance directly impacts user satisfaction and revenue. Even a small slowdown leads to abandonment. To ensure a seamless user experience, it is crucial to conduct performance testing and design specific performance test cases for the search system, especially in web environments where high traffic and concurrent users can affect efficiency, scalability, and stability.
Key Performance Tests
1. Baseline Response Time
Search meets defined SLA under ideal conditions.
2. Response Time Under Load
System remains stable as concurrency increases.
3. Spike Testing
Handles sudden bursts of traffic.
4. Stress Testing
Identify the breaking point and recovery behavior.
5. Concurrency Testing
No race conditions or inconsistent responses.
6. Caching Efficiency
Cached queries return faster; invalidation is correct.
7. Indexing Speed
New or updated items appear within expected timeframes.
8. Large Result Set Handling
No UI freeze or backend degradation.
9. Complex Query Performance
Queries with many tokens or filters remain performant.
10. Filter + Search Performance
Filters should not cause exponential slowdowns.
11. Failure Mode Behavior
Clear, user-friendly error handling during outages.
12. Timeout Handling
Predictable fallback states.
13. Load Balancer & CDN Behavior
Consistent routing and no cross-region mismatches.
14. Logging & Monitoring Reliability
Slow or failed searches are logged and observable.
15. Performance Consistency Over Time
No degradation during peak hours or background indexing.
User Experience & Accessibility Test Cases
Even with perfect logic, poor UX can make search feel broken. Ensuring a positive user experience means the search functionality should enhance user experience by working seamlessly across different devices and helping users quickly find relevant information. These tests verify usability, clarity, and accessibility.
Key UX & Accessibility Tests
1. Search Bar Visibility
Clear placement and easy to find across breakpoints.
2. Placeholder & Guidance
Clear text and screen reader-friendly.
3. Keyboard Navigation
Search must be fully usable without a mouse.
4. Mobile Keyboard Behavior
Correct keyboard is triggered and doesn’t obscure the field.
5. Search Suggestions UX
No lag, flicker, or poor positioning.
6. Zero-Results UX
Helpful suggestions and contextual messaging.
7. Consistent Layout
No broken cards, stretched images, or misaligned text.
8. Screen Reader Support
ARIA roles, labels, and logical reading order.
9. Color Contrast & Focus States
WCAG compliance.
10. Perceived Speed
Instant feedback and clear loading indicators.
11. Infinite Scroll UX
No jumps, duplicates, or broken lazy-loading.
12. Recent Searches Behavior
Correct persistence rules and deletion options.
13. Filter State Visibility
Clear indication of active filters.
14. Error Messaging UX
Readable, non-technical, and actionable.
15. Cohesiveness of Search Flow
Query → Results → Filters → Item → Back flow remains consistent.
How to Test Search Functionality More Efficiently With BugBug
Manually testing search functionality is repetitive, slow, and fragile. Search UIs often include dynamic lists, asynchronous rendering, and frequent data changes—making traditional automation brittle.
BugBug helps QA teams automate search testing with stable, maintainable flows, minimizing flakiness and setup overhead. Automating test cases for search functionality increases efficiency, accuracy, and scalability, ensuring reliable and secure search experiences for users. BugBug is among the best tools for automating and managing search test cases, making it easier for teams to maintain high-quality search features.
BugBug also enables QA teams to efficiently write test cases for search scenarios, supporting a structured approach to comprehensive and effective testing.
How BugBug Improves Search Testing
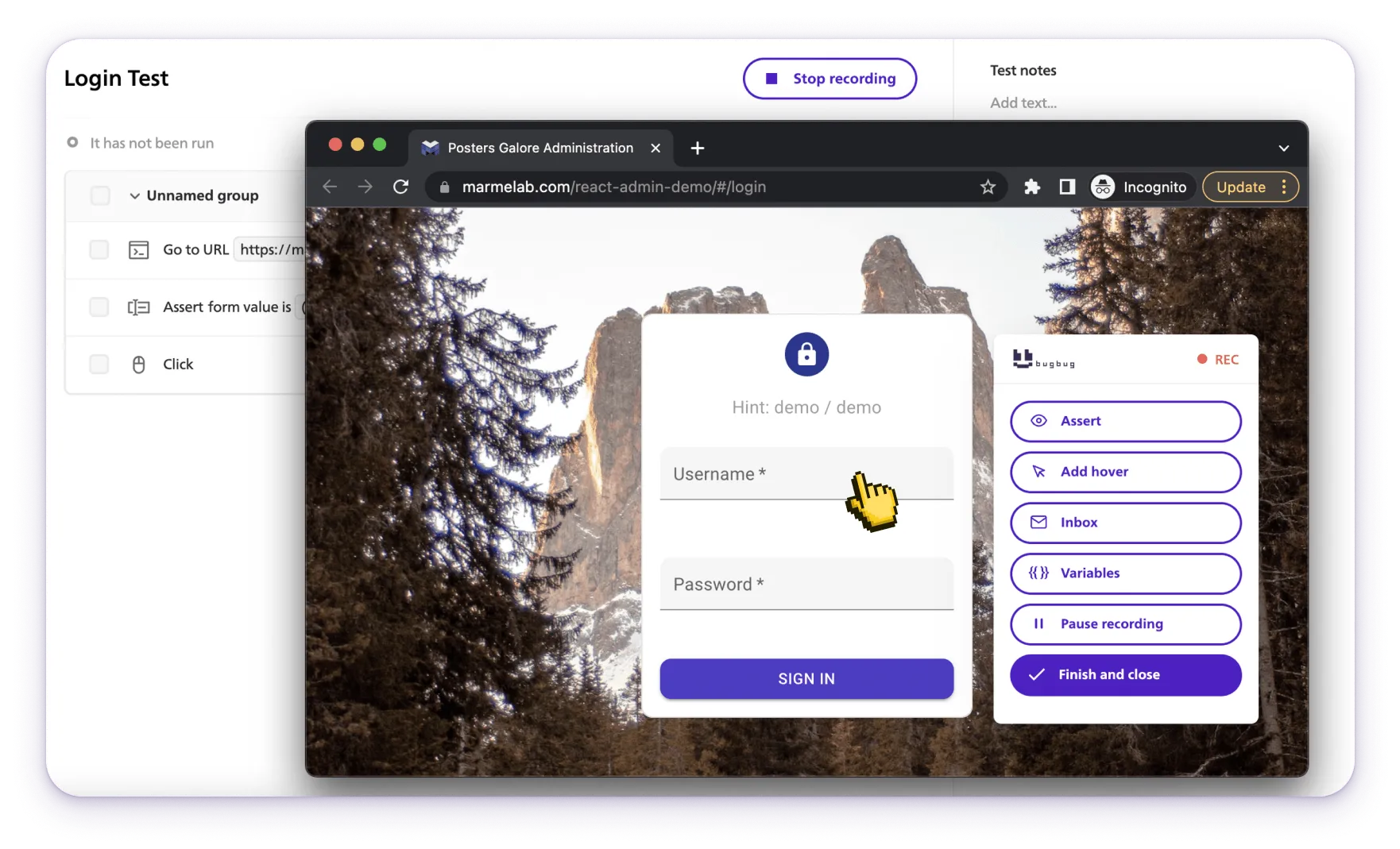
1. Quick Automation of Typical Search Flows
Type query → press Enter → validate results
All done without code.
2. Combine Text & Visual Assertions
Verify:
- keyword presence
- correct thumbnails
- layout integrity
- correct URLs
3. Data-Driven Search Tests
Run the same flow with multiple keywords without duplicating tests.
4. Automatic Stabilization of Dynamic Elements
BugBug waits for UI stability, reducing flaky tests around loaders and animations.
5. Reliable Filter & Sorting Automation
Validate interaction-heavy flows without selector fragility.
6. Scheduled Cloud Runs
Catch regressions early by running search tests hourly or daily.
7. CI/CD Integration
Block deployment if search functionality regresses.
8. Low-Maintenance Test Architecture
BugBug’s resilient element detection reduces maintenance cost dramatically.
Last Thoughts
In the end, testing search functionality is really about protecting the user experience. Whether you're validating how an empty search query is handled, ensuring autocomplete suggestions point users toward relevant products, or confirming that logical operators consistently refine search results, every detail matters—especially on e-commerce platforms where relevance directly affects revenue. A reliable search system must return consistent results across different versions, support different languages, and behave predictably even in difficult edge cases. QA teams need the ability to test sorting options, verify fallback behavior, and run tests repeatedly with easy maintenance as the product evolves. With a tool like BugBug, you can automate complex flows, capture detailed reports, and confidently validate everything from autocomplete behavior to how users refine search results—all while keeping your test suite lean, stable, and ready for whatever comes next.
Happy (automated) testing!