Selenium has long been regarded as the go-to automation testing tool for QA professionals. Its open-source nature and support for multiple programming languages have made it a popular choice among software testing teams.
However, as with any technology, the automation tool with its limitations. In this article, we will delve into the disadvantages of Selenium and explore alternative solutions that address these challenges.
🤖 Summarize this article with AI:
💬 ChatGPT 🔍 Perplexity 💥 Claude 🐦 Grok 🔮 Google AI Mode
🎯 TL;DR - Selenium Disadvantages
- Selenium is a powerful, open-source tool for automating web applications, but it comes with hidden costs and requires significant setup and maintenance.
- Despite its versatility in supporting multiple programming languages and browsers, Selenium has limitations such as lack of native UI testing and challenges with dynamic web elements.
- Selenium often requires integration with third-party tools for comprehensive testing, making it less of an all-in-one solution for test automation.
- Alternatives like low-code or codeless tools offer simpler, more accessible automation options for teams without deep programming expertise.
- 🎯 TL;DR - Selenium Disadvantages
- Key Aspects of Selenium
- Disadvantages of Selenium
- The Hidden Costs Behind 'Free'
- UI Testing
- Beyond the Basics: Selenium's Need for Complements
- The Infrastructure Puzzle
- Slower Test Development: The Price of Precision
- A Parallel Universe of Development
- The Continuous Testing Conundrum
- The Exclusivity of Technical Expertise
- Isolated Yet Connected
- When Community Support Doesn't Cut It
- A Barrier to Broader Team Involvement
- The Stability Issue in Modern Web Development
- Reporting: The Missing Piece
- The Long Road to ROI
- Why is Selenium so hard to use for end-to-end testing?
- How BugBug Makes Testing Simple
- What's the Alternative?
Key Aspects of Selenium

Selenium stands out as a highly prominent open-source tool in the realm of web testing, particularly known for its capabilities in automation and browser interaction.
Fundamentally, Selenium is an open-source framework designed to facilitate the testing of web applications. The essence of Selenium automation testing lies in its ability to interact with different web elements, making it a go-to solution for automating browser actions for testing purposes.
The use of Selenium spans various aspects of web testing. Selenium WebDriver, a key component of the Selenium suite, is instrumental in driving browsers natively as a user would, enabling the testing of a wide range of web applications.
Another important aspect is the Selenium test case, the fundamental unit of testing in Selenium, which allows testers to define specific scenarios for automated testing.
The features of Selenium are quite extensive, including support for multiple browsers and operating systems, making it a versatile tool for web application testing.
- Cross-Browser Compatibility: Selenium supports test execution on different browsers like Chrome, Firefox, Safari, Internet Explorer, and Edge. This allows developers and testers to ensure that web applications function correctly across different web browsers.
- Language Support: Selenium provides support for multiple programming languages including Java, C#, Python, Ruby, Perl, and JavaScript. This means that testers can write their test scripts in any of these languages, making Selenium highly flexible and accessible to a broad range of users.
- Multiple Components:
- Selenium WebDriver: It's the main component of Selenium and provides a programming interface to create and execute test cases. WebDriver interacts directly with the browser without any intermediary, unlike its predecessor Selenium RC.
- Selenium IDE (Integrated Development Environment): It's a Firefox and Chrome plugin that allows for record-and-playback of interactions with the browser, which is useful for creating test scripts quickly without needing to write code.
- Selenium Grid: It's used to run tests in parallel across different machines and browsers simultaneously, which helps in speeding up the testing process. - Platform Independence: Test scripts written in Selenium can be executed on different operating systems like Windows, Mac OS, and Linux.
- Community Support: Being an open-source tool, it has a large community of developers and testers who contribute to its continuous improvement and provide a wealth of resources, including documentation, forums, and tutorials.
- Integration Capabilities: Selenium can be integrated with other tools like TestNG and JUnit for managing test cases and generating reports. It can also be integrated with tools like Jenkins or Bamboo for continuous integration and with tools like Appium for mobile testing.
- Use Cases: It's primarily used for automated functional testing and regression testing but is also suitable for creating robust, browser-based regression automation suites and tests.
💡 TIP
Disadvantages of Selenium
The Hidden Costs Behind 'Free'
First off, let's talk about cost.
Is Selenium free? Yes, but don't let that fool you.
When you factor in the time and resources needed to set it up and get it running, especially in time-sensitive projects, the 'free' tag comes with its price.
For teams predominantly skilled in manual testing, the transition to Selenium isn't just about adopting a new tool; it's about choosing between upskilling your current team or bringing in new tech-savvy members --- a decision that's not always straightforward.
UI Testing
Selenium doesn't provide built-in support for testing the user interface of web applications.
While it can interact with web elements in the underlying code, it relies on element locators and does not fully capture the visual layer that users interact with. This means that Selenium tests may pass even if there are visual bugs or regressions that real users would immediately notice.
Additionally, the slightest change in an element locator can cause Selenium tests to fail, leading to false positives.
Additionally, it lacks native functionality for handling Windows-based popups and desktop applications, and requires programming skills for test script development, posing a barrier for those without a technical background.
Beyond the Basics: Selenium's Need for Complements
Moving on, Selenium isn't your one-stop shop for all things test automation.
It relies heavily on a host of third-party tools and libraries. Think of it as needing a good supporting cast of frameworks, like TestNG, to shine in end-to-end testing scenarios.
While Selenium does not inherently provide reporting capabilities, it offers the flexibility to integrate with various frameworks and tools to produce detailed and insightful test reports.
This flexibility for many users can be seen as an advantage. It's one of the reasons why Selenium remains a popular choice for web automation testing despite the extra effort required to set up comprehensive reporting.
Automate your tests for free
Test easier than ever with BugBug test recorder. Faster than coding. Free forever.
Get started
The Infrastructure Puzzle
Then there's the challenge of infrastructure, particularly if you're looking at parallel testing. The financial and logistical aspects of setting up additional testing machines can be daunting, and these requirements can change with every new project.
Slower Test Development: The Price of Precision
Crafting stable and maintainable tests in Selenium is no small feat. It demands a certain level of proficiency in programming, which means your test development might not be as swift as you'd like.
A Parallel Universe of Development
Here's a thought-provoking point: implementing Selenium can sometimes feel like you're running a parallel development project. The technical efforts, along with the need for continuous updates and maintenance, can be overwhelming, particularly for smaller or medium-sized companies in their growth phase.
The Continuous Testing Conundrum
In the world of continuous delivery and DevOps, Selenium's code-based approach can be a hindrance. It's challenging to shift testing left, a move crucial for continuous integration and testing.
The Exclusivity of Technical Expertise
Selenium's code-centric nature inadvertently gates off non-programmers from the test creation process. In an ideal world of continuous delivery and DevOps, where quality is everyone's responsibility, this exclusivity can be a drawback.
Isolated Yet Connected
Despite its ability to integrate with various development tools, Selenium's lack of solid integrations with Test Management and Requirement Management solutions means test automation often remains an island of its own.
When Community Support Doesn't Cut It
The Selenium community is indeed helpful, but for large-scale enterprise projects demanding quick resolutions and privacy, community support might not be enough.
A Barrier to Broader Team Involvement
With Selenium, test scripts are often not the easiest for the non-technical crowd to grasp, creating a barrier to broader team involvement in the test automation process.
The Stability Issue in Modern Web Development
Modern web development's heavy use of AJAX and asynchronous programming can lead to stability issues in Selenium tests, further complicated by the difficulty in maintaining these test scripts.
Reporting: The Missing Piece
One significant gap in Selenium's capabilities is its lack of intuitive, comprehensive test reporting, making it harder to share results with stakeholders and understand test outcomes at a glance.
The Long Road to ROI
Lastly, considering the high initial time investment and the slow pace of test development, the return on investment with Selenium can be a long journey, particularly for smaller teams.
Automate your tests for free
Test easier than ever with BugBug test recorder. Faster than coding. Free forever.
Get started
Why is Selenium so hard to use for end-to-end testing?
Selenium has been around for nearly two decades and is often the first tool teams think of when automating browser tests. It’s powerful, widely supported, and flexible — but when it comes to end-to-end testing in modern agile teams, Selenium often proves more painful than helpful.
Here’s why:
- Complex setup and infrastructure
Running Selenium tests usually means managing WebDriver binaries, configuring browser drivers, and often setting up Selenium Grid for parallel execution. For small teams without a dedicated QA infrastructure engineer, this complexity quickly becomes overwhelming. - Slow execution
Selenium tests interact with browsers in a way that introduces significant overhead. Combined with network waits, long test flows, and flaky selectors, execution speed suffers dramatically compared to lightweight frameworks. - High maintenance costs
Selenium scripts are code-heavy and brittle. Small UI changes — like renaming a button or moving an element — can cause entire suites to break. Maintaining dozens or hundreds of scripts consumes valuable engineering time. - Steep learning curve
Unlike newer tools with visual recorders or simplified APIs, Selenium requires strong programming skills. QA engineers without a developer background struggle to get productive, and onboarding new team members is slow. - Flakiness
Because Selenium interacts at the browser level, tests often fail for reasons unrelated to actual bugs (e.g., timing issues, environment instability). These false negatives erode trust in automation suites.
The result is that teams end up spending more time fighting the tool than testing the product. That’s why many modern QA engineers look for alternatives — frameworks and platforms designed to be faster, lighter, and easier to maintain in agile workflows.
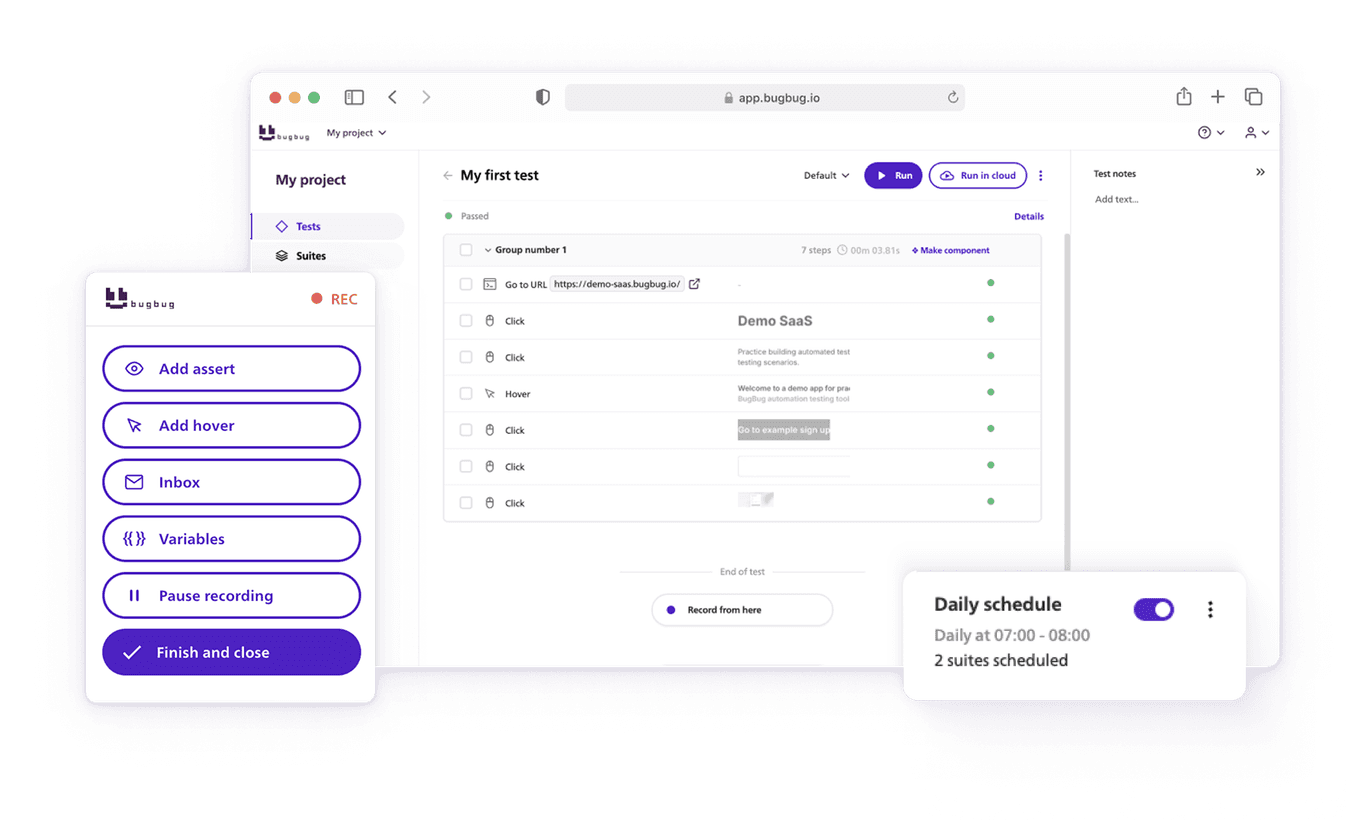
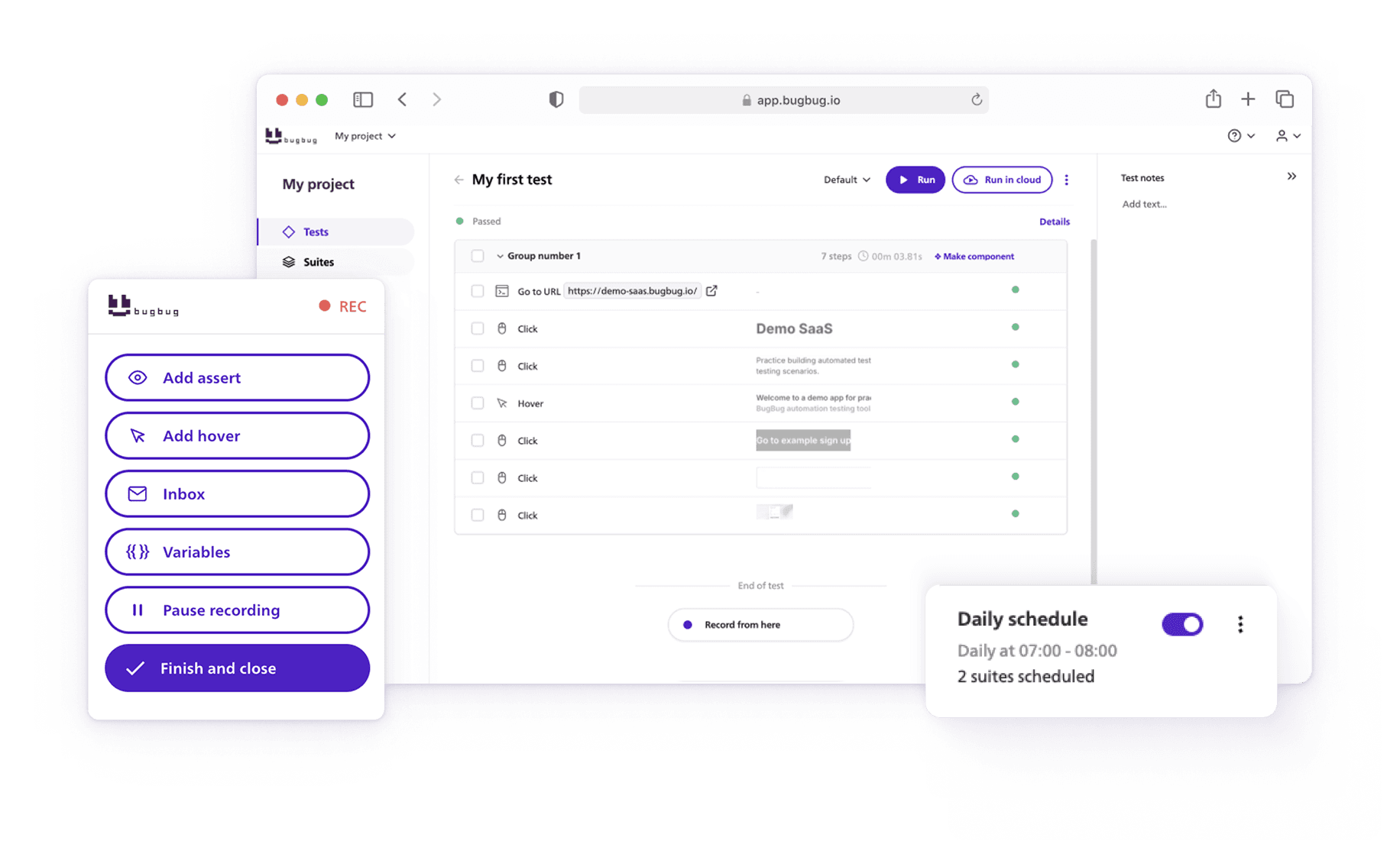
How BugBug Makes Testing Simple
Where Selenium demands complex setup, steep learning curves, and constant maintenance, BugBug was designed with simplicity and speed in mind. Instead of wrestling with grids, drivers, and brittle scripts, teams can focus on testing what matters: user workflows.
Here’s how BugBug removes the pain points of Selenium:
- Zero infrastructure overhead
No Selenium Grid, no Docker containers, no VMs. BugBug works right out of the box, letting teams run tests locally or in the cloud without any extra setup. - Faster execution
BugBug’s lightweight architecture eliminates the slow browser-driver communication layer, making test runs significantly quicker. This is especially valuable in CI/CD pipelines where speed directly impacts release velocity. - Easy test creation and maintenance
With BugBug’s intuitive recorder and Edit & Rewind feature, creating and updating tests is as simple as clicking through a workflow. When the UI changes, tests can be edited quickly without digging into code-heavy scripts. - Built-in email testing
Instead of wiring up mail servers or third-party services, BugBug lets you validate password resets, confirmations, and notifications right inside your test suite. - Designed for small teams
Startups and lean QA teams benefit from BugBug’s minimal learning curve. It empowers both developers and non-technical testers to contribute without requiring deep programming expertise.
In short: BugBug gives you the power of end-to-end testing without the Selenium headaches. It’s faster, lighter, and built for the agile workflows modern teams rely on.
What's the Alternative?
Low-code and codeless solutions have emerged as popular Selenium alternatives, especially for teams looking to automate web application testing without the steep learning curve associated with traditional coding.
💡 TIP
Tools like BugBug enable users to create automation flows without writing any code.
These tools are designed to simplify the test automation process, making it accessible to users with limited programming skills. Most modern tools provide a codeless environment for creating automated UI tests.
👉 Check our No-code Automation Testing guide.
Happy (automated) testing!